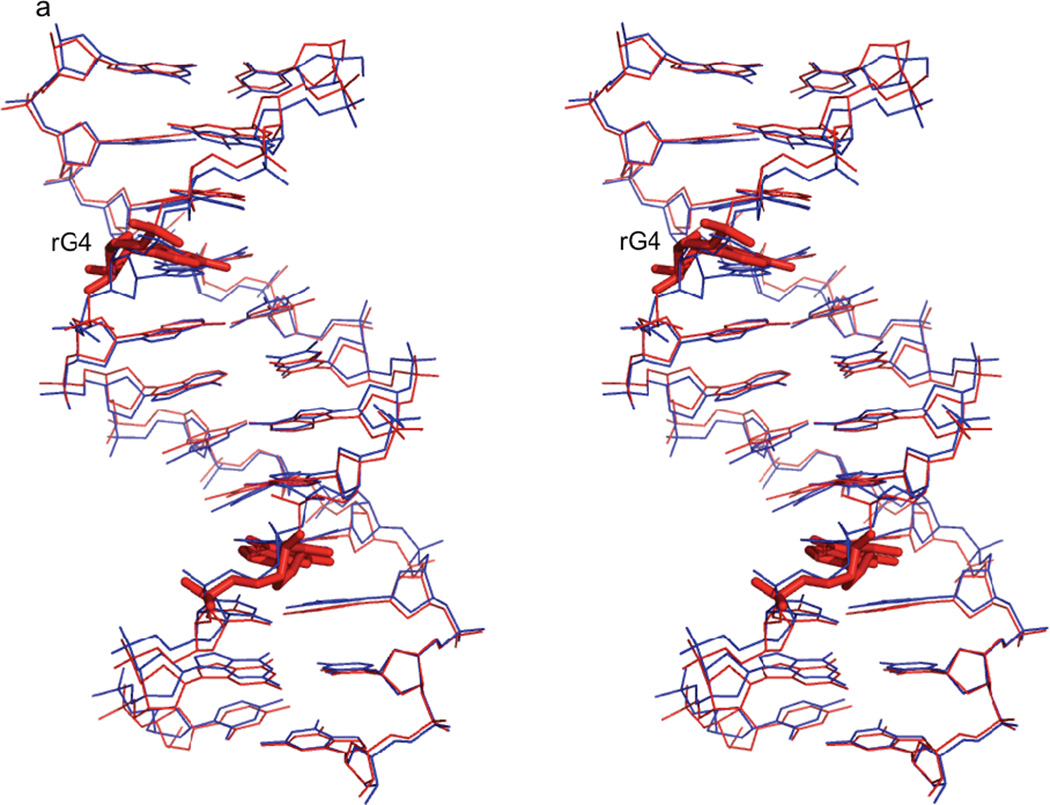
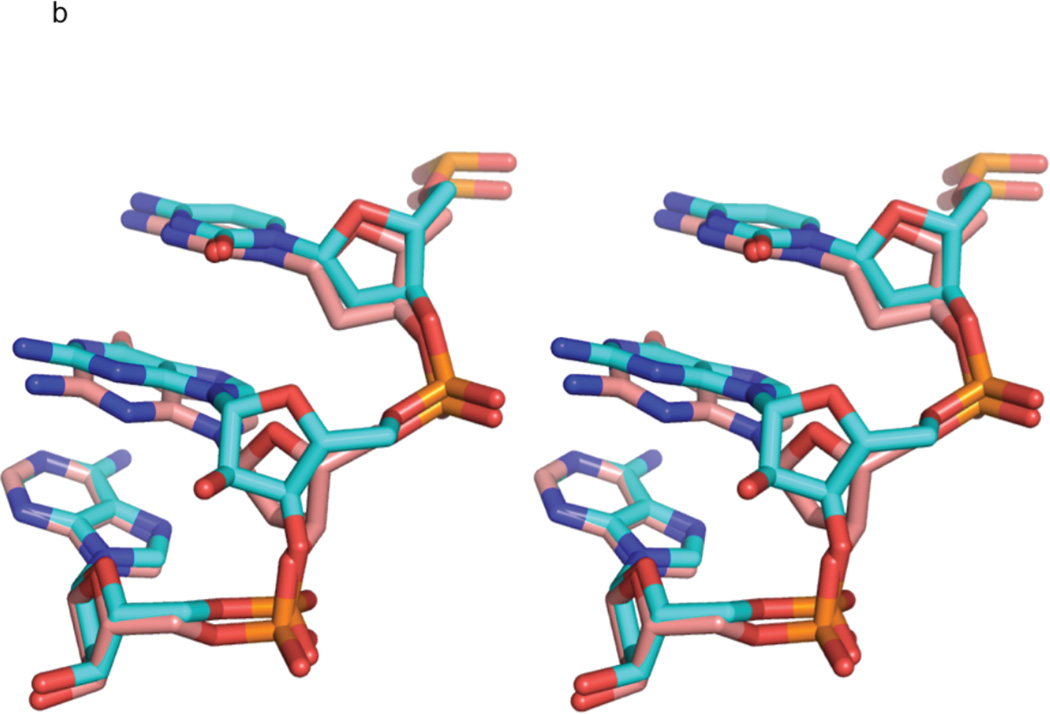
Figure 3. Comparison of rG4-substituted and unsubstituted Dickerson dodecamer NMR solution structures.
a) Stereo view of the superposition of the lowest energy rG4-DNA (red) and dd-DNA (blue) structures. The structures superimpose with an RMSD of 0.750 Å for all atoms. The rG4 ribonucleotide and its complement are highlighted as a stick rendering. The dd-DNA structures were computed using the same XPLOR-NIH simulated annealing calculation as the rG4-DNA with a similar set of experimental restraints as described in the text. The view is into the major groove along the major helical axis. 3b) A stereo view of nucleotides C3, rG4/G4, and A5 of the lowest energy rG4-DNA (cyan) and dd-DNA (coral) structures, showing the slight change in guanosine base position and sugar pucker from C2'-endo in the dd-DNA structure to C3'-endo in the rG4-DNA structure. The view is looking into the minor groove.