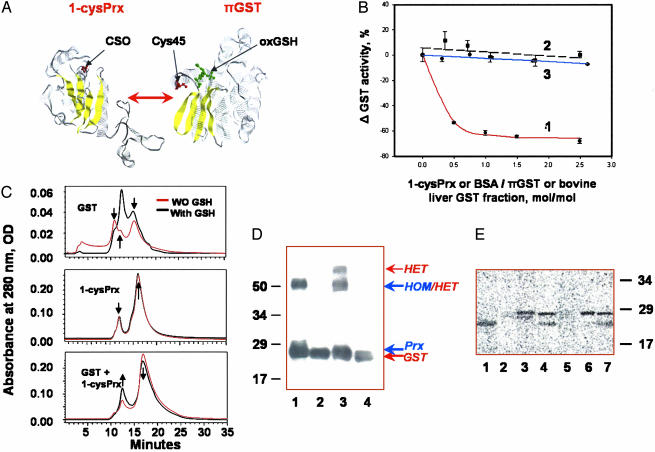
Fig. 2.
Heterodimerization and glutathionylation of 1-cysPrx. (A) Monomers of 1-cysPrx and πGST [with associated GSH sulfonate (oxGSH) in green] showing selected cysteine moieties in red (22, 27). Yellow indicates β-sheets. (B) GST enzymatic activity with 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene in the presence of increasing concentration of proteins: Trace 1, rat 1-cysPrx added to πGST; trace 2, BSA added to πGST; trace 3, rat 1-cysPrx added to liver GST that lacks the π isoform. (C) Size exclusion HPLC of a rat 1-cysPrx and πGST, and their equimolar mixture before (red trace) and after (black trace) preincubation with 10× excess of GSH. The arrows indicate characteristic peaks and their changes. The molecular mass standards used for calibration were chymotrypsinogen A (bovine pancreas) (25 kDa, RT = 15.5 min), chicken ovalbumin (44 kDa, RT = 13.25 min), BSA (67 kDa, RT = 11.25 min), and transferrin (81 kDa, RT = 10 min). (D) Detection of 1-cysPrx/πGST heterodimerization by crosslinking with sulfo-SBED. Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE, transferred to Immobilon-P membrane, and detected with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin. Lanes: 1, mixture of 1-cysPrx plus biotinylated 1-cysPrx; 2, same as lane 1 after reduction with DTT; 3, biotinylated 1-cysPrx plus πGST; 4, same as lane 3 after reduction with DTT. The molecular mass markers are shown on the left, and the presumed positions of the homo- (HOM) and heterodimer (HET) are shown on the right. (E) 35S autoradiogram of recombinant 1-cysPrx and πGST, and their combination after incubation with G[35S]H. Lanes: 1, authentic πGST; 2, oxidized rat 1-cysPrx (inactive); 3, oxidized and denatured rat 1-cysPrx; 4, rat 1-cysPrx plus πGST; 5, oxidized bovine (inactive) 1-cysPrx; 6, oxidized and denatured bovine 1-cysPrx; 7, bovine 1-cysPrx with GST. The molecular mass markers are indicated on the right.