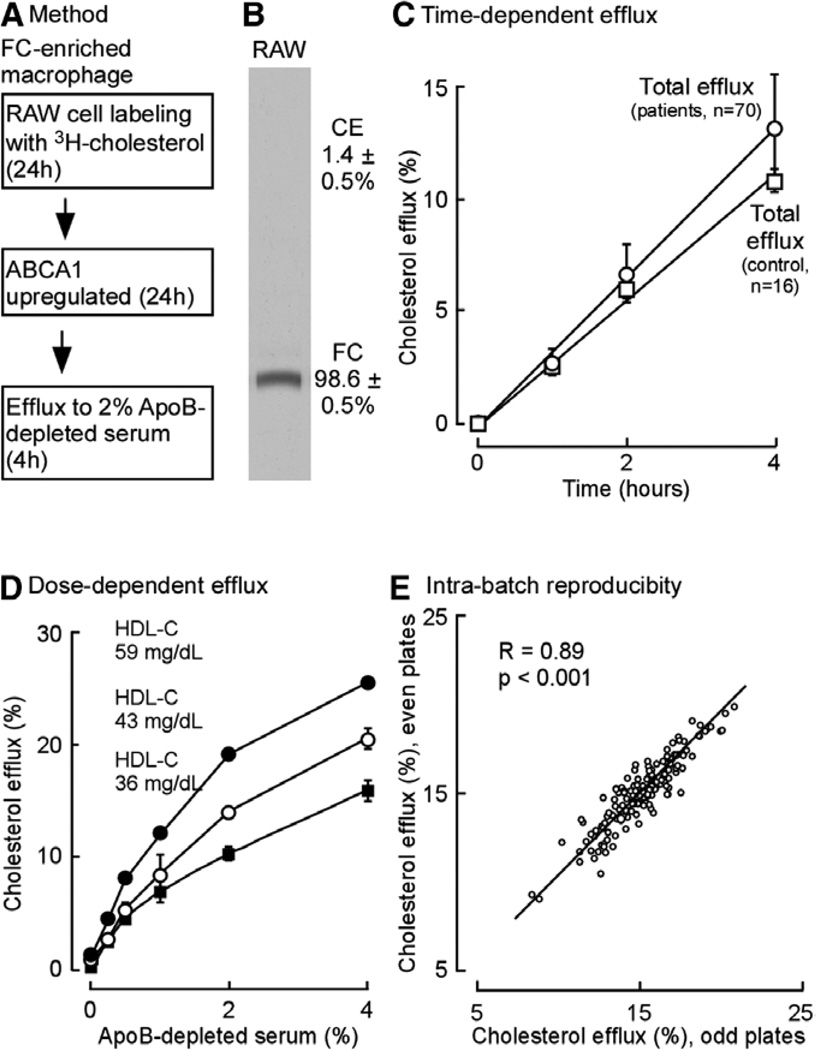
Figure 2.
Cholesterol efflux assay methodology and characterization. A, General scheme of cholesterol efflux assay used. B, Autoradiogram and quantification of cellular [14C] free cholesterol (FC) and [14C]cholesterylester (CE) found in [14C] cholesterol-loaded macrophage RAW cells. C, Time course of total cholesterol efflux to 2% serum, vol/vol (pool made from random sampling of the indicated number [n] of patient samples from the outpatient cohort and control serum pool, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol [HDLc] 59 mg/dL, used). D, Dose-dependent efflux for total cholesterol from RAW264.7 cells incubated with the indicated final concentration (vol/vol) of apolipoprotein B (apoB)–depleted human serum as cholesterol acceptor. Serum pools with different HDLc levels as indicated were used. Values shown are an average of at least triplicate measurements. E, Intra batch apoB-depleted serum total cholesterol efflux assay reproducibility was plotted as even plates vs odd plates in the same batch, Spearman correlation coeffi-cient (R=0.89; P<0.001). ABCA1 indicates ATP-binding cassette transporter A1.