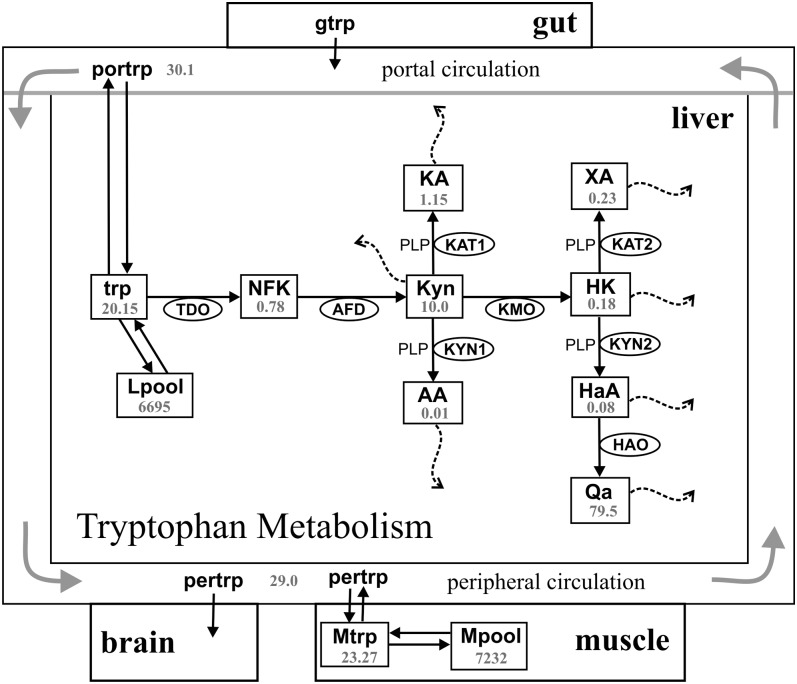
FIGURE 1.
Diagram of the model. The rectangles represent substrates, and the ellipses contain the acronyms of enzymes. The 2 instances of KYN and KAT are labeled differently because they have different substrates and (possibly) different velocities. Transport of tryptophan from the gut to the serum and from the serum to the muscle or liver compartments is by the l-amino acid transporter. Steady state concentrations (μmol/L) are shown. AA, anthranilic acid; AFD, aryl formamidase; gtrp, tryptophan in the gut; HaA, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; HAO, 3-hydroxynalic acid oxygenase; HK, 3-hydroxykynurenine; KA, kynurenic acid; KAT, kynurenine aminotransferase; KMO, kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; Kyn, kynurenine; KYN, kynureninase; Lpool, tryptophan incorporated into proteins in liver; Mpool, tryptophan incorporated into proteins in muscle; Mtrp, tryptophan in muscle; NFK, N-formyl-kynurenine; Qa, quinolinic acid; pertrp, tryptophan in the peripheral circulation; PLP, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate; portrp, tryptophan in portal circulation; TDO, tryptophan 2,3- dioxygenase; trp, tryptophan; XA, xanthurenic acid.