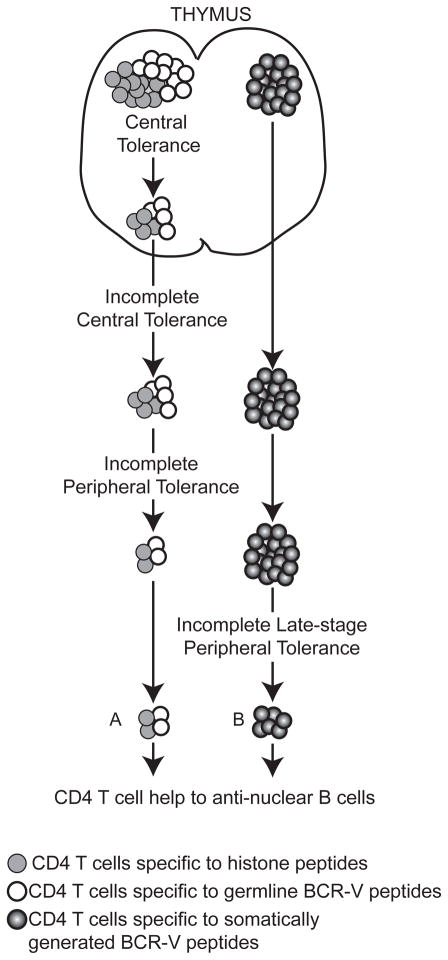
Figure 2. Origin of T cell help for anti-nuclear B cells.
Source of T cell help to antinuclear B cells in SLE. (A) Defect in central and/or peripheral T cell tolerance in a lupus-prone background allows autoreactive CD4 T cells reactive with peptides from histones and/or germline-encoded BCR-V regions to escape self-tolerance and help anti-nuclear B cells. (B) Self-tolerance in CD4 T cells is intact with respect to peptides from histones and germline-encoded BCR-V regions; however CD4 T cells that recognize somatically generated BCR-V region-derived peptides provide a source of help to autoreactive B cells. Autoimmune prone-genetic backgrounds might have a defective regulation of this type of T-B interaction, resulting in the production of anti-nuclear antibodies by an autoimmune B cell.