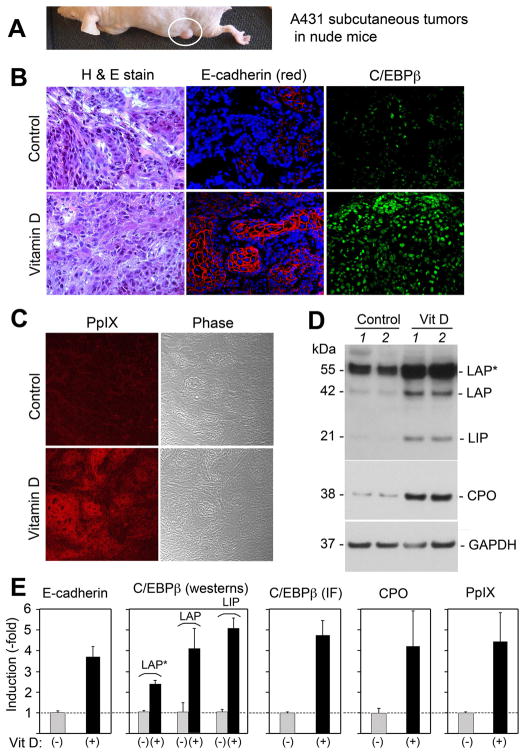
Figure 1. C/EBP transcription factors, the CPO enzyme, and PpIX are increased in subcutaneous A431 tumors undergoing Vitamin D-induced differentiation in vivo.
Subcutaneous A431 tumors (A) were treated for 3 days with calcitriol (Vitamin D), 5 μg/kg or with saline alone (Control). (B) Tumors were harvested and analyzed as follows: Left panels, Standard histological staining; Middle panels, Immunofluorescence (IF) staining for E-cadherin (red) and nuclear DAPI, counterstain (blue); Right panels, IF for C/EBPβ (green); (C) Confocal imaging for PpIX (red), and the same field shown in phase-contrast; (D) Western analyses for C/EBPβ isoforms, CPO, and GAPDH. Tissues from Vitamin-D treated tumors and control tumors, each from a different mouse, were analyzed. (E) Quantitative analysis of relative expression was analyzed from multiple tumors, in separate graphs as follows (method of analysis in parentheses): E-cadherin (by IF); C/EBPβ, individual isoforms (by westerns); C/EBPβ total levels (by IF); CPO protein (by westerns); PpIX levels (by confocal microscopy). Western analyses were normalized to GAPDH. Bars represent mean ± SD, n = 3 tumors each.