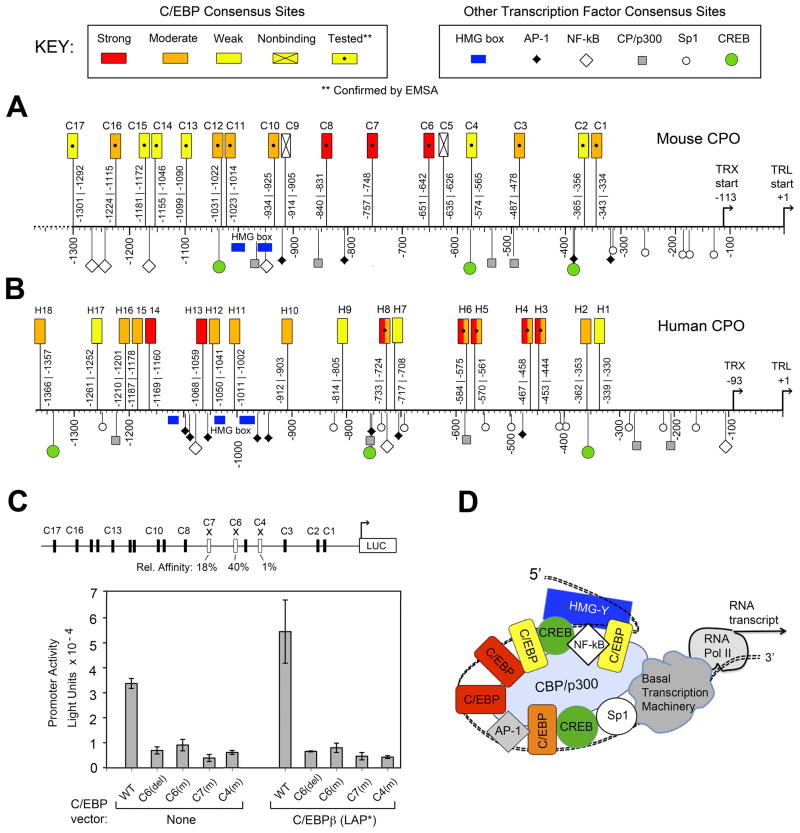
Figure 5. Locations of C/EBP binding sites, and evidence for cooperative interactions, in the upstream regulatory region of mouse and human CPO genes.
Alignments of the (A) mouse CPO, and (B) human CPO regulatory upstream gene regions. Each promoter sequence is aligned relative to the translation (TRL) and transcription (TRX) start sites. Locations of the C/EBP sites are indicated by rectangles. Locations of some other transcription factor binding motifs (identified by Transfac search algorithm) are shown by other symbols. See Key for explanation. (C) Mutation of individual C/EBP sites within an intact 946 bp mCPO promoter abrogates transcriptional activity. When a wildtype reporter-luciferase reporter construct (pSK-946Luc) is transfected into LNCaP cells, cotransfection with C/EBPβ further induces transcriptional activity (compare bars 1 and 6). When C/EBP sites are deleted (del) or disrupted by single-site mutations (m), overall activity is dramatically reduced. Error bars, range of duplicates. Schematic (top) shows the mCPO promoter sites chosen for mutation (open rectangles), with their relative binding affinities prior to mutation (from Table 1) shown beneath. Mutated sequences are found in Supplementary Table 1. (D) Hypothetical model of promoter-enhancer system (enhanceosome) regulating CPO transcription; see text for details.