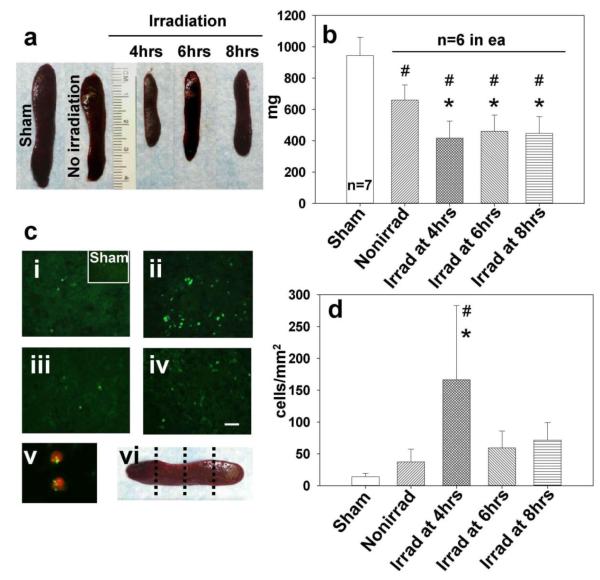
Fig. 3.
The effect of irradiation on spleen 7 days after stroke. (a) Representative photographs of spleens from sham surgery group and nonirradiated MCAO (right panel) and irradiated spleens. (b) Graph bars indicate reduced weight of irradiated spleens after ischemia, most profoundly at 4 hrs time of delay (*p<0.05 vs. nonirradiated, #p<0.05 vs. sham, ANOVA). (ci) In the sham operated and nonirradiated ischemic group only a limited number of TUNEL-positive cells was found (magnification bar: 30μm). (cii) Strong TUNEL positivity of splenic cells was associated with radiation at 4 hrs post-ischemia. Splenic irradiation performed at 6 hrs (ciii) and 8 hrs (civ) post ischemia resulted in fewer TUNEL positive cells than seen in the 4 hrs irradiation group. (cv) The photograph (blown up X4) of double stain involving TUNEL (fluorescein) and T cell marker (Texas Red) indicates T cells as apoptotic spleen cells following irradiation at 4 hrs. (cvi) Levels of spleen sectioning for immunofluorescence and cell count. (d) Bar graphs showing significant increase in the number of splenic apoptotic cells in the 4 hrs group vs. nonirradiated (*p<0.05) and vs. sham-operated rats (#p<0.05)