FIGURE 8.
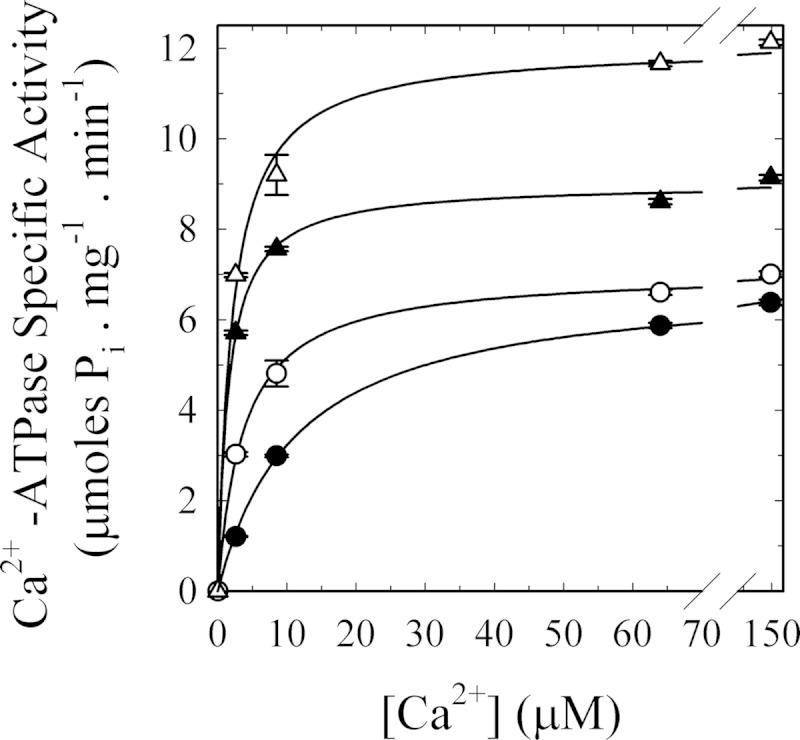
[Ca2+] dependence of G-actin effect on human erythrocyte PMCA Ca2+-ATPase activity. Ca2+-ATPase activity was measured at different [Ca2+] in the presence of the following: 100 nm calmodulin (▴) as a positive control for PMCA activation; 5 μm G-actin (○); 100 nm calmodulin plus 5 μm G-actin (Δ), or buffer (●) as the basal condition. The reaction was started by the addition of 2 mm ATP concomitant with the addition of the effector/buffer. The reaction medium contained 120 mm KCl, 30 mm MOPS-K (pH 7.4 at 25 °C), 3.75 mm MgCl2, 70 μg/ml C12E10, 10 μg/ml phosphatidylcholine, 1 mm EGTA, and enough CaCl2 to give the desired final [Ca2+]free. PMCA concentration was 0.8 μg/ml. Pi release was determined by the continuous method of Webb (46). Values are the mean ± S.E. from three different experiments. When not apparent, error bars are within the symbols. The values of K0.5 and Vmax for the different treatments are as follows: basal conditions 11.4 ± 0.4 μm and 6.9 ± 0.1 μmol of Pi·mg−1·min−1, respectively; addition of 100 nm CaM 1.5 ± 0.1 μm and 9.0 ± 0.1 μmol of Pi·mg−1·min−1, respectively; addition of 5 μm G-actin 3.7 ± 0.2 μm and 7.1 ± 0.1 μmol of Pi·mg−1·min−1, respectively; addition of 100 nm CaM plus 5 μm G-actin 2.1 ± 0.3 μm and 12.1 ± 0.3 μmol of Pi·mg−1·min−1, respectively.
