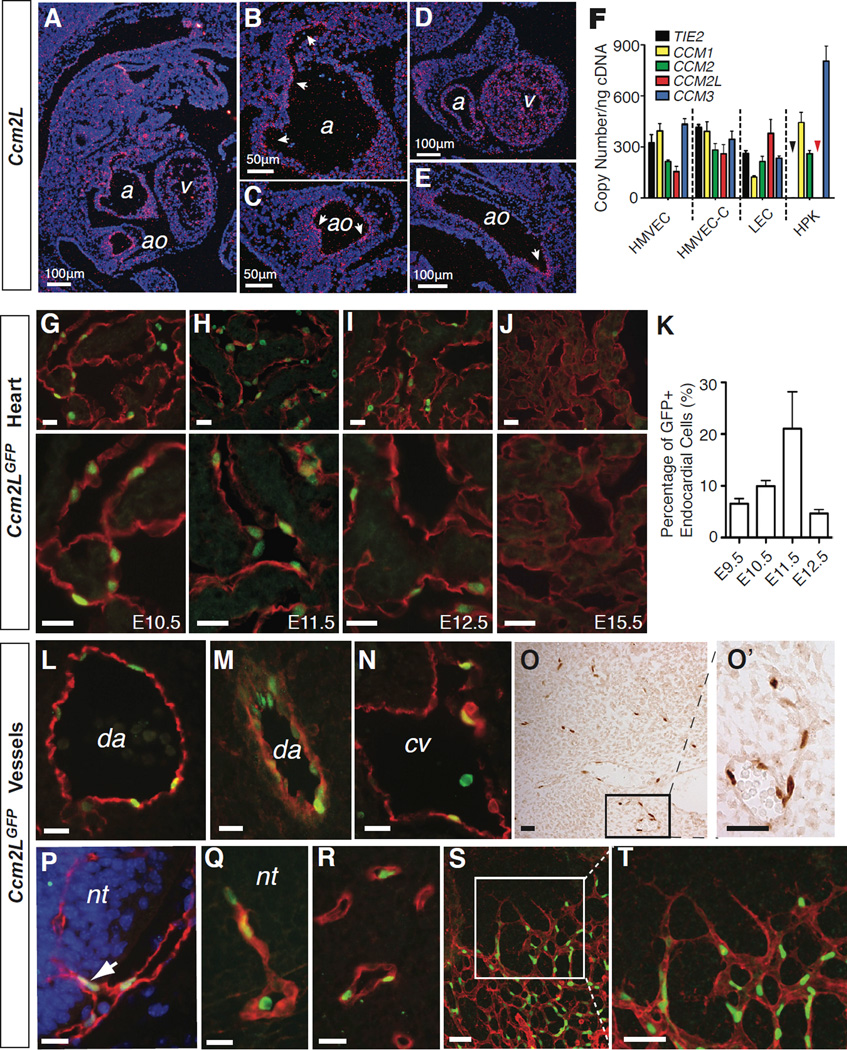
Figure 2. Ccm2L is expressed in endothelial cells that participate in active cardiovascular growth.
A–E. In situ hybridization reveals endothelial-specific expression of Ccm2L. Shown are saggital sections of an E11.5 mouse embryo. Ccm2L signal is shown in pink (arrows) and DAPI staining of cell nuclei in blue. ao, aorta; cv, cardinal vein; a, atrium; v, ventricle. F. Quantitative RT-PCR measurement of mRNA transcripts encoding CCM1, CCM2, CCM2L, CCM3 and the endothelial-specific control gene TIE2 in cultured human microvascular endothelial cells from the skin (HMVEC) and heart (HMVEC-C), dermal lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC), and human primary keratinocytes (HPK) is shown. The black and red arrowheads indicate that no expression of TIE2 or CCM2L was detected in HPKs. N=4; error bars indicate SEM. G–K Ccm2LGFP expression in the endocardium. Shown are low (above) and high (below) magnification images of cardiac trabeculae from E10.5 -E15.5 hearts following immunostaining for GFP (green) and the endothelial cell marker PECAM (red). K. Quantitation of Ccm2LGFP-expressing endocardial cells during mouse cardiac development. N=5; error bars indicate SEM. L–N. Expression of Ccm2LGFP in the dorsal aorta (da) and cardinal vein (cv) at E10.5. O–T Ccm2LGFP is expressed in the endothelial cells of nascent vessels. Ccm2LGFP was frequently detected in non-lumenized endothelial extensions of existing vessels (O), such as those that invade the neural tube (nt) at E10.5-E11.5 (P, Q), and microvasculature (R), and in newly formed microvasculature of the neonatal retina (S, T). Scale bars indicate 20 µm unless otherwise indicated. See also Supp. Fig. 1 and Supp. Table 1.