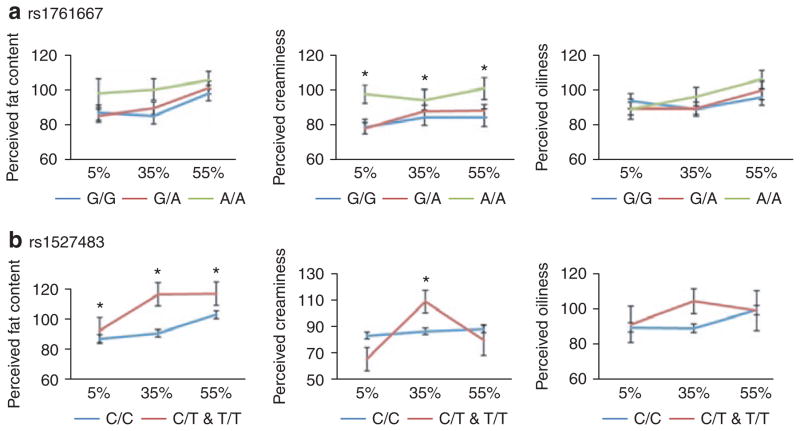
Figure 1.
Oral fat perception ratings for 5, 35, and 55% fat-by-weight Italian salad dressings as a function of CD36 genotype at (a) rs1761667 and (b) rs1527483. (a) Ratings for perceived fat content, creaminess, and oiliness as a function of rs1761667 genotype and fat concentration (5, 35, and 55% fat-by-weight). There was a main effect of rs1761667 genotype on ratings of perceived creaminess (F(2,305) = 5.5; P < 0.01). A/A individuals perceived greater creaminess than G/A (P = 0.03) and G/A (P = 0.02) individuals (post hoc, Scheffé). (b) Ratings for perceived fat content, creaminess, and oiliness as a function rs1527483 genotype. There was a main effect of rs1527483 genotype on ratings of perceived fat content (F(1,306) = 4.5; P = 0.02). C/T and T/T individuals (n = 20) tended to perceive greater fat content than C/C individuals (n = 288). There was a significant interaction between rs1527483 genotype and fat concentration on ratings of perceived creaminess (F(2,306) = 3.3; P = 0.04; interaction effect). C/T and T/T individuals rated the 35% fat salad dressing as creamier than C/C individuals (P < 0.05; post hoc, Scheffé).