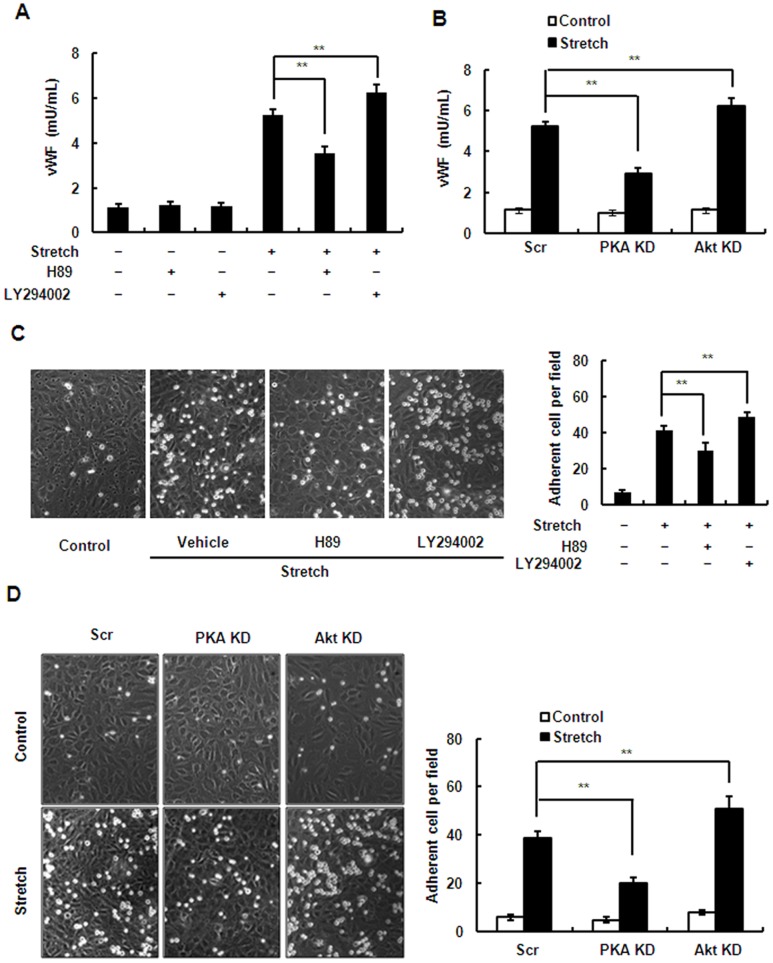
Figure 8. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway increases stretch-induced WPB exocytosis and leukocyte adhesion while inhibition of PKA has the opposite effect.
(A) vWF release from HUVECs pretreated with H89 (50 µM), LY294002 (50 µM) or vehicle (DMSO) in response to stretch. (B) vWF release from HUVECs expressing scrambled (Scr), PKA-targeting (PKA KD), or Akt1/2-targeting (Akt KD) shRNA under continuous stretch. (C) Left: HL-60 cell adhesion to HUVEC monolayers after stretch, pretreated with H89 (50 µM), LY294002 (50 µM) or vehicle (DMSO). Right: quantitative analysis of HL-60 adhesion. (D) Left: HL-60 cell adhesion to HUVECs expressing scrambled (Scr), PKA-targeting (PKA KD), or Akt1/2-targeting (Akt KD) shRNA after stretch. Right: quantitative analysis of HL-60 adhesion. Results are representative of 3 individual experiments and expressed as mean ± S.D. (n = 4), **p<0.01.