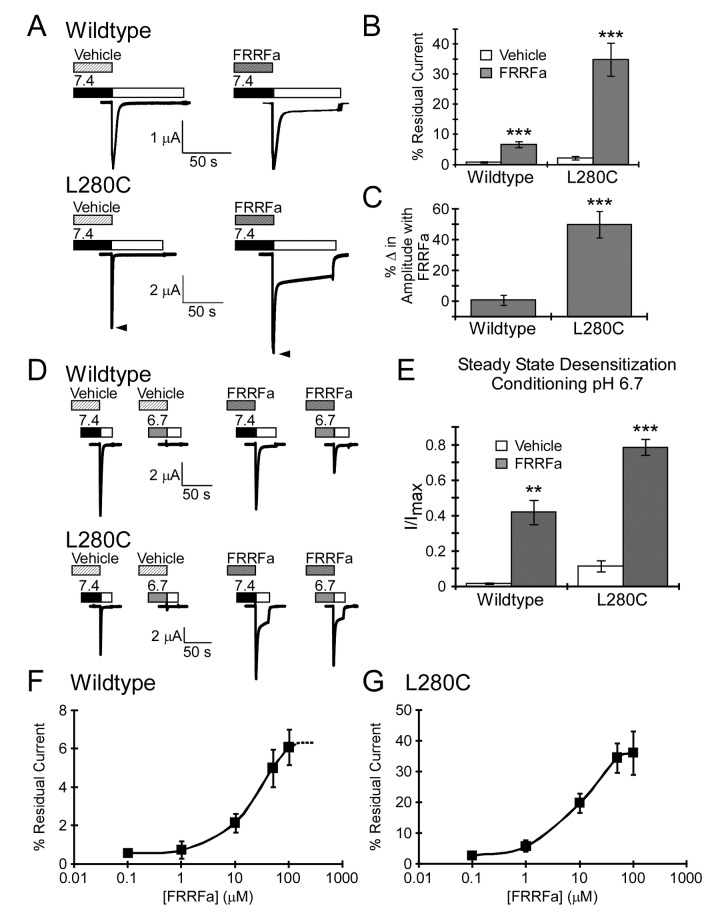
Figure 4. FRRFa modulation of L280C.
A. FRRFa increases residual current of wildtype and L280C. FRRFa (100 µM) was applied for 1 minute at pH 7.4 prior to activation with pH 5.0. For L280C, arrowheads highlight the FRRFa-induced increase in peak current amplitude. B. Quantification of residual current (n = 14-17). C. Quantification of FRRFa modulation on pH 5.0-evoked peak current amplitude. The percent change in amplitude was determined by subtracting the pH 5.0-evoked peak current amplitude of vehicle from the pH 5.0 evoked peak current amplitude evoked after FRRFamide modulation and normalizing to the vehicle peak current amplitude from the same cell (n = 17-25). D. Representative trace of FRRFa modulation on steady-state desensitization. 100 µM FRRFa or vehicle was applied for 1 minute at basal pH 7.4 and again during the 2 minute incubation with conditioning pH 6.7. Proton-gated current was evoked with pH 5.0 (white bar). E. Quantification of FRRFa modulation of steady-state desensitization (n = 4). F–G. FRRFamide concentration response curve for wildtype ASIC1a (F) and L280C (G). The effect of FRRFamide on residual current was assessed. Our data suggest that 100 µM FRRFa induced a maximal response on wildtype ASIC1a as 300 µM FRRFa was not significantly different from 100 µM FRRFa (n = 5, p = 0.69 paired Student’s t-test, difference between 100µM and 300µM was 10.42% ± 11.25%; data not shown). Based on this information, the calculated EC50 for wildtype ASIC1a was 20 ± 4 µM and 14 ± 4 µM for L280C (n = 6-8, p = 0.34). Data are mean ± SEM. “**” and “***” indicates p-value < 0.01 and 0.001 respectively.