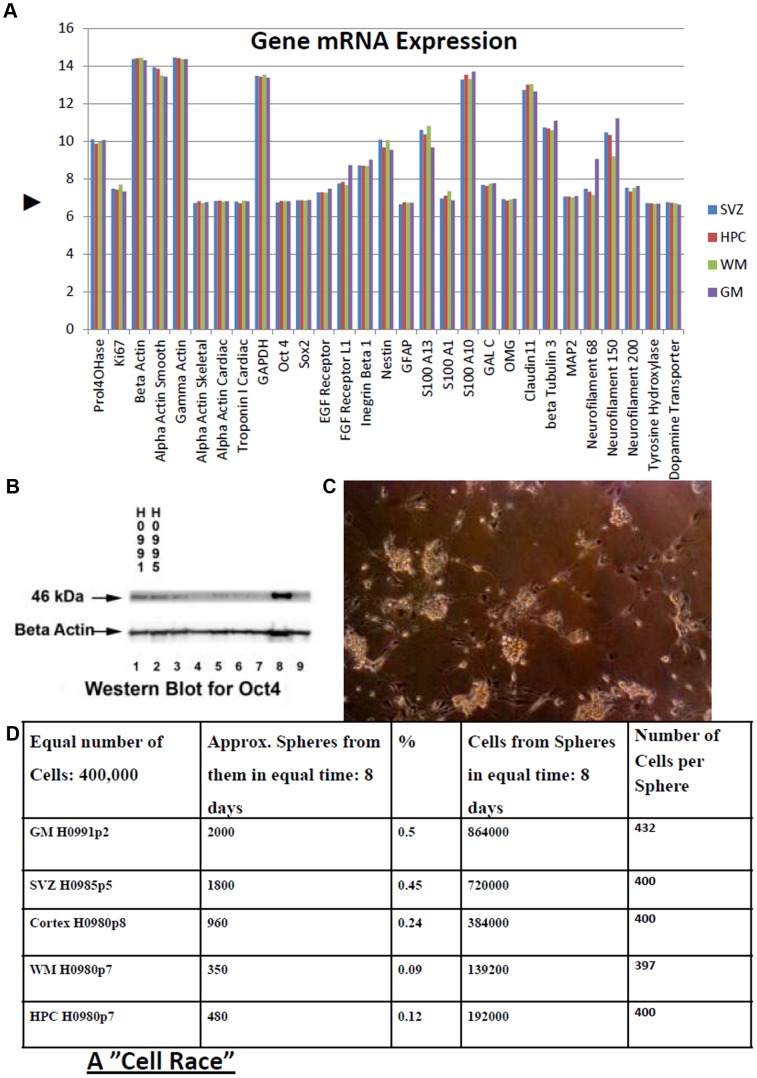
Figure 6. Characteristics of human brain stem cells.
A. mRNA Phenotype of four groups of brain derived stem cells. mRNA levels in stem cell cultures (mean of three humans) comparing those derived from Subventricular Zone (SVZ), Hippocampus (HPC), White Matter (WM) and Grey Matter (GM). These are some common genes some of which were already assessed using immunohistochemical techniques as we have described above. Data are from the same microarray platform and were processed together. Ordinate axis units are mean probe strength (Log2) recorded for the genes specified on the co-ordinate axis. Microarray data were ‘quantile normalised’. ▸: Basal level of transcription. Markers: Housekeeping: Prolyl-4-hydroxylase, β-actin, γ-actin, GAPDH. Dividing cells: KI67. Stem cells: OCT 4, SOX2, EGF receptor, integrin-β1, nestin. Neurons: β-tubulin3, MAP2, neurofilament. Glia: GFAP, S100. Oligodendrocytes: OMG, claudin11, GALC. Smooth muscle: α-actin smooth. Skeletal muscle: α-actin skeletal. Cardiac muscle: α-actin cardiac, cardiac troponin I. Dopaminergic cells: Tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine transporter. B. Western blot confirmed robust expression of stem cell ‘pluripotency’ marker OCT 4 (POU5f1). 40 µg total protein was run on each lane. Lanes 1 and 2: normal samples: 1, HPC, 2, SVZ; Lanes 3–9: tumor stem cells. C. Cells (grown adherently) and then subsequently plated in neurosphere-forming conditions. D. From Table in D, it can be seen that though the sphere generating cells from the different sources varied in density, the cells generated from them had similar growth ability (number of cells per sphere).