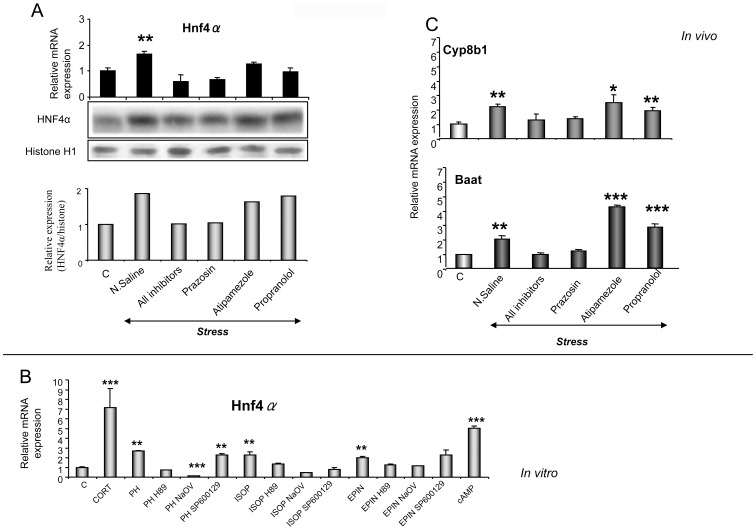
Figure 4. Stress-induced effect on Hnf4a expression.
A. Following restraint stress alone or coupled with AR-antagonists hepatic Hnf4a mRNA levels were analysed in wild-type mice by qPCR. HNF4α protein was measured in liver nuclear fractions by Western blot analysis. Histone H1 served as a loading control. B. Cyp8b1 and Baat mRNA levels were analyzed in the livers of wild-type mice by qPCR following treatment with either restraint stress alone or coupled with AR-antagonists (dark bars). C. Hnf4a mRNA levels were determined by qPCR following treatment of primary hepatocyte cultures with either corticosterone (CORT), epinephrine (EPIN) or AR-agonists for 24 hours. Primary hepatocytes were also treated with AR-agonists in combination with the JNK inhibitor, SP600125 (SP), or the PKA inhibitors, H89 or sodium orthovanadate (NaOV). Values were normalized to β-actin and are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 8–10). Comparisons were between controls and stress- or drug-treated mice. AR: adrenergic receptor, C: control, N. Saline: normal saline, All inhibitors: mice were treated with all AR-antagonists prior to stress, Prazosin (alpha1-AR antagonist), Atipamezole (alpha2-AR antagonist), Propranolol (beta-AR antagonist), PH: Phenylephrine (alpha1-AR agonist), ISOP: Isoprenaline (beta-AR agonist). Group differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferonni's test. *P<0.025, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.