Figure 4. EF24 regulates radiation-induced NFκB dependent hTERT transactivation, transcription and confers radiation induced cell killing.
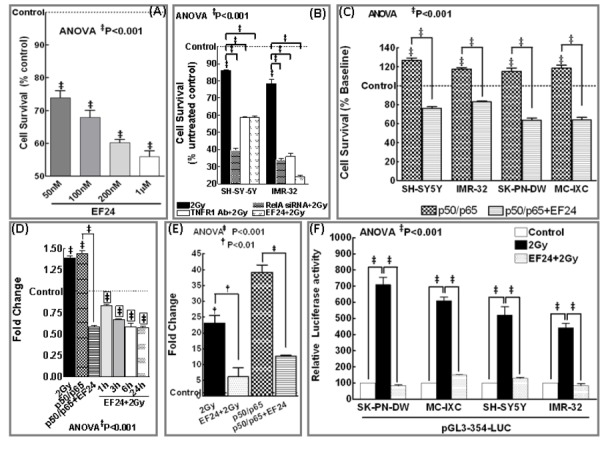
(A) MTT analysis showing survival response in human SH-SY5Y cells exposed to EF24 (50, 100, 200nM, 1μM). Induced inhibition of cell survival was compared to mock-IR control. (B) Histograms of MTT analysis showing cell survival response in SH-SY5Y and IMR-32 cells either exposed to IR (2Gy) with or without EF24, transfected with RelA siRNA and exposed to IR or treated with TNFR1 Ab and exposed to IR. (C) MTT analysis showing inhibition of NFκB dependent survival response in NFκB (p50/p65) overexpressed human SH-SY5Y, IMR-32, SK–PN–DW and MC-IXC cells with EF24 treatment. Groups were compared using ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-hoc correction. Histograms showing hTERT mRNA expression assessed by QPCR analysis in (D) SH-5Y5Y and (E) IMR-32 cells mock-irradiated, exposed to 2Gy, treated with EF24 for 3h followed by 2Gy exposure and harvested after 1, 3, 6 and 24h, transfected with p50/p65 with or without EF24 treatment. The ΔΔct values were calculated by normalizing the gene expression levels to internal housekeeping gene (β-actin), compared between groups, and the relative expression level was expressed as a fold change over mock-IR cells. ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc correction was used to compare between groups. (F) Luciferase reporter assay: SH-SY5Y, IMR-32, SK–PN–DW and MC-IXC cells transfected with pGL3-354-Luc construct and either mock irradiated, exposed to 2Gy, treated with EF24 and exposed to 2Gy were harvested at 24h post-IR and analyzed by luciferase assay. Groups were compared using ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-hoc correction. Data shown represent the mean and SD of three independent experiments.
