Figure 7. Intra-tumoral EF24 regress tumor growth in NB xenograft mice.
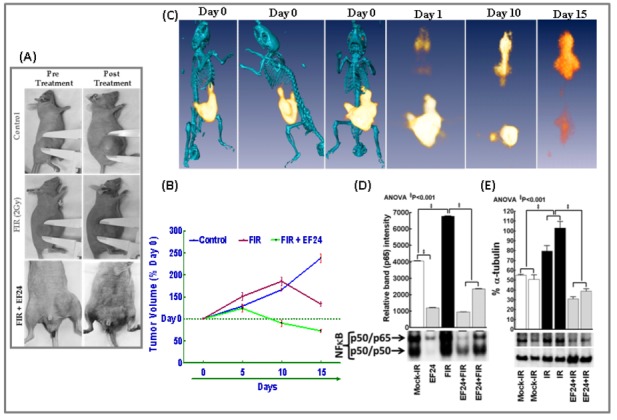
(A) Representative photographs showing variations in tumor size prior to and after treatment in NB xenograft mice. The mice were either mock-irradiated, exposed to FIR (2Gy/D for 5D/Wk to a total dose of 20Gy) or treated with daily dose of intra-tumoral EF24 (200µg/Kg) in conjunction with FIR. (B) Line plot of NB tumor volume depicting incessant NB progression in mock-IR animals and significant NB regression after EF24 administration in conjunction with FIR exposure as opposed to FIR exposure alone. (C) FDG-PET-CT over-imposed images showing intra-tumoral EF24 administration associated tumor regression in athymic nude mice bearing NB xenograft. (D) NFκB DNA-binding activity in NB xenografts exposed to FIR, treated with intra-tumoral EF24 with or without FIR exposure. The nuclear extracts from treated xenografts were analyzed by EMSA using γ-32p[ATP] labeled NFκB-specific probe. Semi-quantitative densitometry of autorads using Quantity One 1D image analysis (Biorad) showed complete inhibition of FIR-induced NFκBDNA-binding activity in human NB xenografts treated with EF24.Groups were compared using ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-hoc correction. (E) Representative immunoblot and corresponding densitometry showing TNFα levels in mock-irradiated and irradiated (with or without intra-tumoral EF24) NB xenografts. Semi-quantitative densitometry of immunoblots using Quantity One 1D image analysis (Biorad) showing α-tubulin intensity normalized expression of TNFα. Groups were compared using ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-hoc correction.
