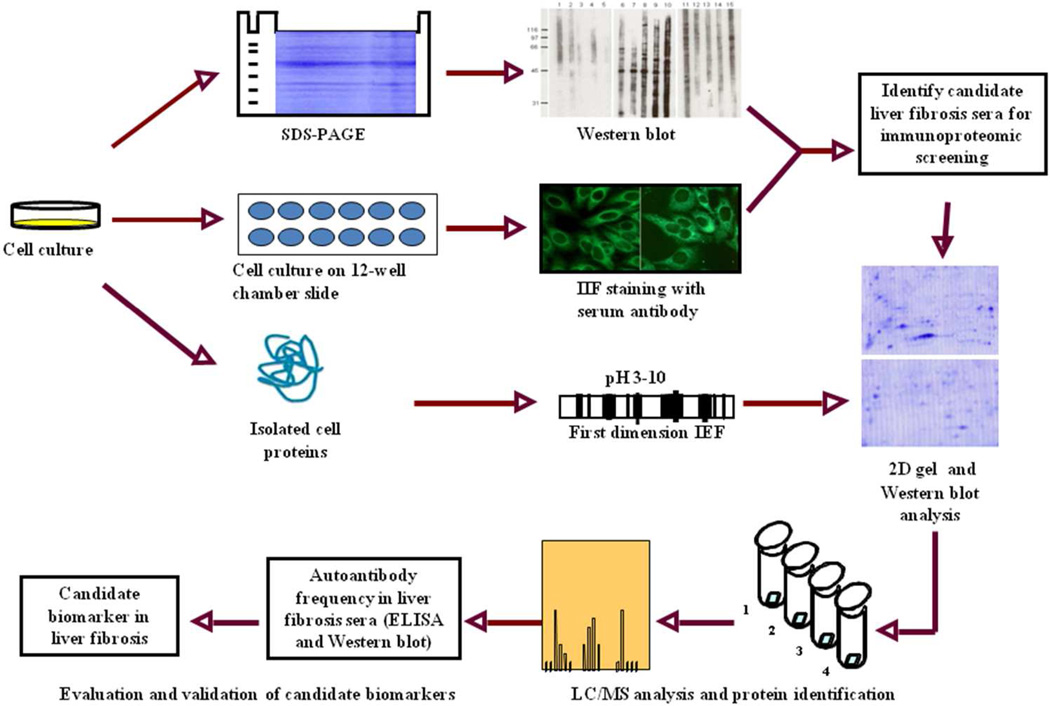
Figure 1. Schematic representation of potential protein biomarker identification in liver fibrosis.
In brief, the sera from liver fibrosis patients and controls were initially examined using extracts of tissue culture cells as source of antigens in Western blot and by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) on whole cells. With these two techniques, we identify sera which have high-titer fluorescent staining or strong signals to cell extracts on Western blot and subsequently use the antibodies in these sera as probes in immunoproteomic screening. Cell extract of cultured human cells was also applied onto the first dimension gel (isoelectrofocusing gel), and subsequently loaded onto the second-dimension gel (2D-SDS-PAGE). The proteins were transferred to the nitrocellulose membrane or visualized by silver staining or Coomassie brilliant blue staining. After immunoblotting with liver fibrosis sera and control sera, a number of protein spots of interest were excised from the 2-D gels, digested by trypsin, and subsequently analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS). In subsequent studies, we will characterize the identified cellular proteins that are potential biomarkers in liver fibrosis.