Fig. 6.
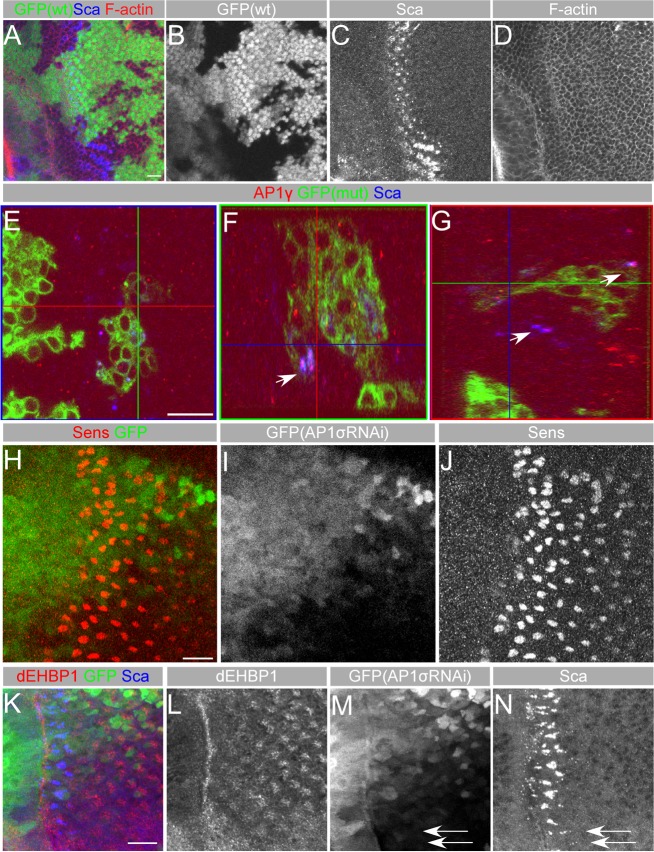
dEHBP1 does not affect the integrity of cytoskeleton but results in the accumulation of AP-1γ along with Sca. (A–D) Loss of dEHBP1 within clones of cells negatively marked by GFP (B) does not affect distribution of fluorescently marked phalloidin, a marker of F-actin (D). (E–G) Loss of dEHBP1 within clones of cells positively marked by nuclear GFP results in accumulation of AP-1γ along with Sca, as evident by the arrows in the YZ (F) and XZ (G) confocal slices of the XY view (E). Please note that AP-1γ appears to colocalize with Sca in wild-type tissue as well, suggesting that Sca vesicles are of AP-1γ identity. (H–J) eyg-Gal4-driven RNAi-mediated knockdown of the AP-1σ subunit of the AP-1 complex in a domain marked by the expression of GFP (I) results in development of supernumerary R8 photoreceptors, as seen by expression of Sens (J) in agreement with previously published data (Kametaka et al., 2012). (K–N) eyg-Gal4-driven RNAi-mediated knockdown of the AP-1σ subunit of the AP-1 complex in a domain marked by the expression of GFP (M) results in intracellular accumulation of Sca (N), in agreement with previously published data (Kametaka et al., 2012), without affecting the subcellular localization of dEHBP1. Scale bars: 10 nm.