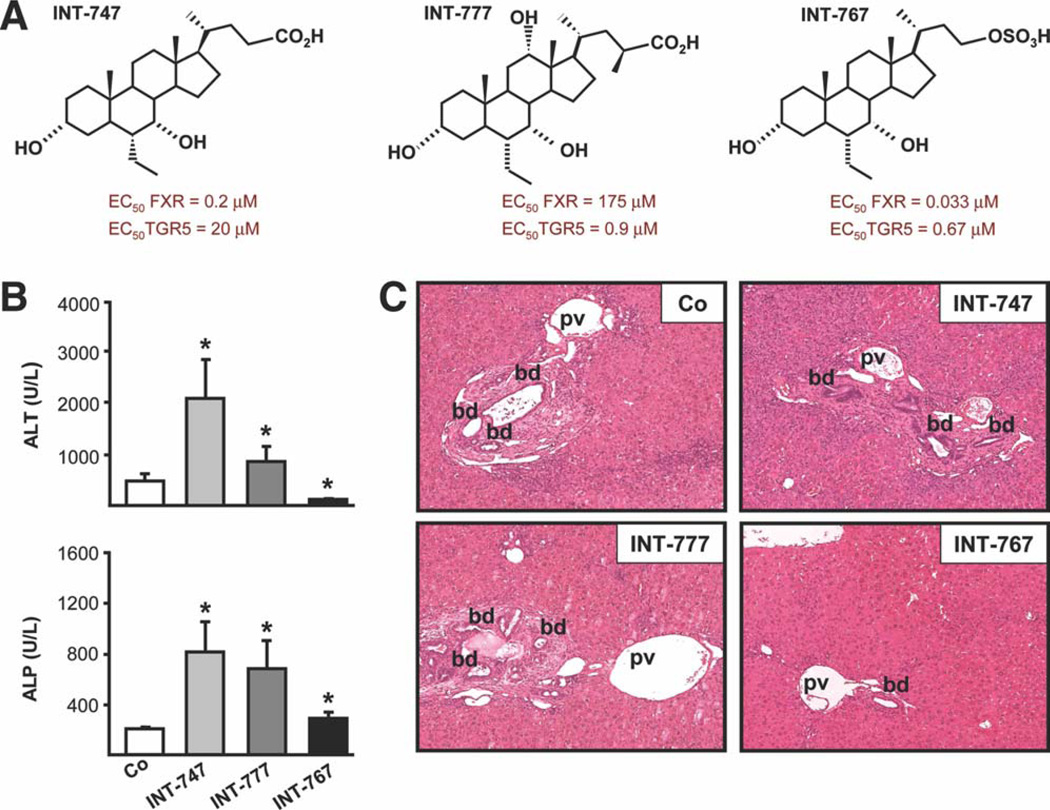
Fig. 1.
Dual FXR/TGR5 agonist INT-767 improves liver injury in Mdr2−/− mice. Mdr2−/− mice were either fed a chow diet or a diet supplemented with the FXR agonist, INT-747, the TGR5 agonist, INT-777, or the dual FXR/TGR5 agonist, INT-767 for 4 weeks. (A) Chemical structures of INT-747, INT-777, and INT-767 compounds with respective FXR and TGR5 EC50. (B) INT-747 and INT-777 increased serum ALT and ALP, whereas INT-767 significantly reduced serum ALT, but not ALP, levels. Means of 6 mice/group ± SD. *P < 0.05 INT-747, INT-767, and INT-777 versus controls. (C) Representative histological pictures of H&E-stained livers. Bile duct proliferation and portal infiltration of inflammatory cells was reduced by INT-767. The INT-747-fed Mdr2−/− mouse showed increased bile duct proliferation, expansion of biliary tract, and accumulation of inflammatory cells. No obvious alterations were detected in the INT-777-fed Mdr2−/− mouse liver. Co, chow-fed littermates; pv, portal vein; bd, bile duct.