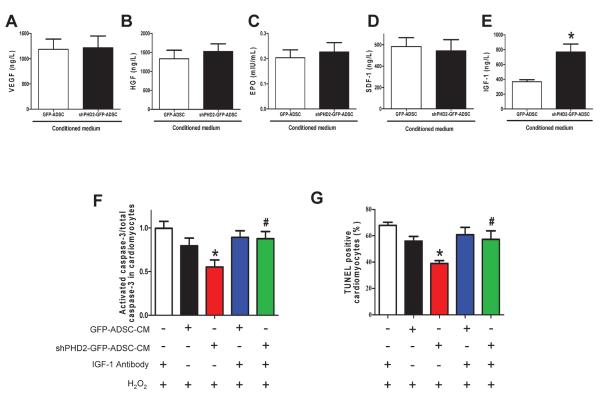
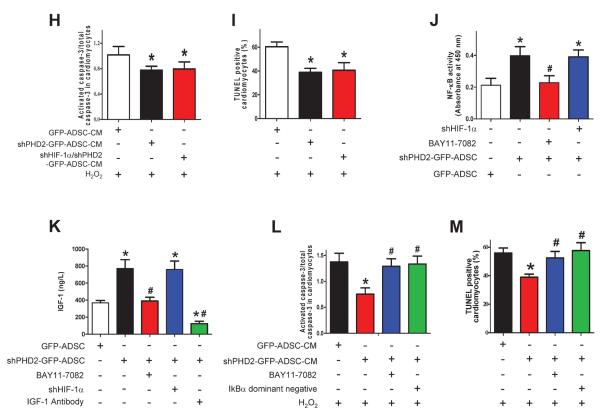
Figure 7.
PHD2 silencing enhances ADSCs paracrine effect by increasing IGF-1 secretion via the NF-κB pathway. A–E: Levels of pro-survival cytokines, VEGF (A), HGF (B), EPO(C), SDF-1 (D) and IGF-1 (E) in ADSCs-CM determined by ELISA assay. N=10, * p<0.05 vs. GFP-ADSCs-CM. F–G: The effect of IGF-1 neutralization and shHIF-1α on ADSC paracrine mediated anti-apoptotic effects on cardiomyocytes. The cardiomyocyte apoptosis was analyzed by Western blotting of activated caspase-3 expression (F) and TUNEL+ rate (G). N=3. * p<0.05 vs. H2O2+IGF-1 antibody; #p<0.05 vs. H2O2+shPHD2-GFP-ADSC-CM. H–I: The anti-apoptotic effect of shPHD2/shHIF-1α-ADSCs-CM on cardiomyocytes, analyzed by Western blotting of activated caspase-3 expression (H) and TUNEL+ rate (I). N=4. * p<0.05 vs. H2O2+GFP-ADSC-CM. J: The effect of HIF-1α and NF-κB inhibition on NF-κB activity in different groups of ADSCs. * p<0.05 vs. GFP-ADSCs; # p<0.05 vs. shPHD2-GFP-ADSCs. K: The effect of HIF-1α silencing and NF-κB inhibition on IGF-1 secretion of ADSCs. For J–K: N=6. * p<0.05 vs. GFP-ADSCs; # p<0.05 vs. shPHD2-GFP-ADSCs. L–M: The effect of NF-κB inhibition on ADSC paracrine mediated anti-apoptotic effect on cardiomyocytes subjected to H2O2. NF-κB activity is inhibited by BAY11-7082 or IκBα dominant negative. The cardiomyocyte apoptosis was analyzed by Western blotting of activated caspase-3 expression (L) and TUNEL+ rate (M). N=3. * p<0.05 vs. H2O2+GFP-ADSC-CM; # p<0.05 vs. H2O2+shPHD2-GFP-ADSC-CM. VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; HGF: hepatocyte growth factor; SDF-1: stromal cell-derived factor 1; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1.