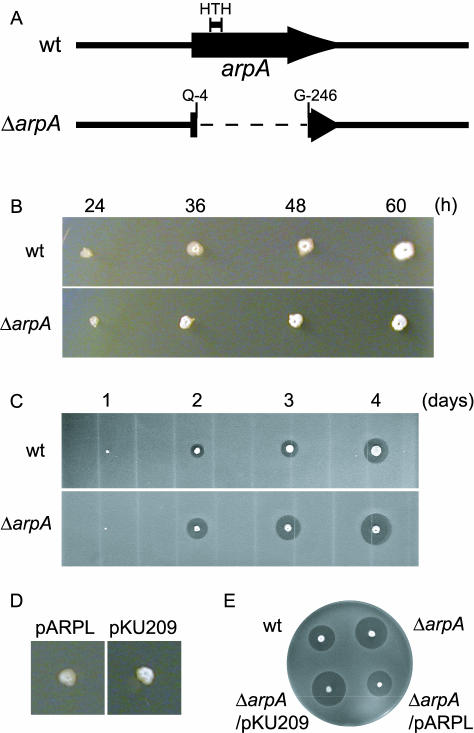
FIG. 1.
Phenotypes of an arpA null mutant, the ΔarpA mutant, of S. griseus. (A) Schematic representation of the structures of arpA on the chromosome of S. griseus IFO13350 (wild type, wt) and an arpA deletion mutant (ΔarpA). ArpA contains a helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA-binding motif near the N terminus. The ΔarpA mutant contains an in-frame deletion from Ala-5 to Gly-245. (B) Effects of the ΔarpA mutation on morphological differentiation. Both strains were inoculated with a toothpick and grown on YMPD agar medium (19) at 28°C for the indicated periods. (C) Effects of the ΔarpA mutation on streptomycin production. Strains were inoculated with a toothpick and grown on Bennett agar medium (10) without glucose at 28°C for the indicated periods. Spores of Bacillus subtilis were then overlaid, and the plates were incubated at 37°C for 1 day. Streptomycin production was detected by the formation of a growth inhibition zone. (D) Morphological differentiation of the ΔarpA mutant harboring pARPL at the normal time. The ΔarpA mutant harboring pKU209, grown for 36 h in the same way as in B, prematurely forms aerial mycelium, whereas the mutant harboring pARPL remains as substrate hyphae. (E) Streptomycin production by the ΔarpA mutant harboring pARPL in the normal yield at the normal time. Strains were grown for 3 days, and streptomycin production was assayed in the same way as in C.