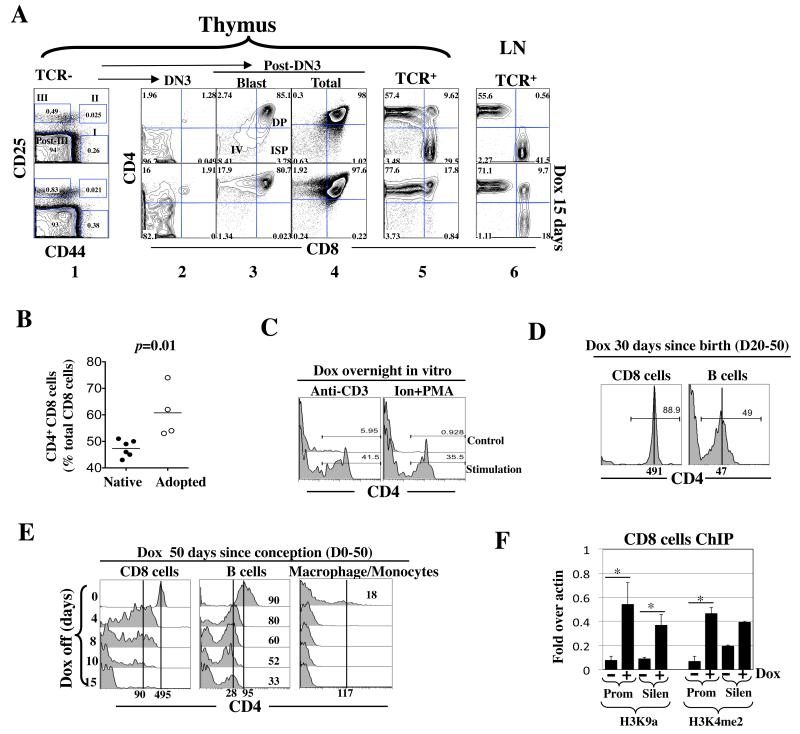
Fig. 4. rtTA induced ectopic CD4 expression.
(A) Adult Cd4*/+; rtTA+/− mice were exposed to Dox (1 mg/ml) for 15 days. Thymocytes were stained for TCR, CD4, CD8, CD25 and CD44 and analyzed as described (33-35). Briefly, the TCR−/lo cells were first resolved into 4 subsets, DN1 (I), DN2 (II), DN3 (III) and post-DN3 (Post-III) based on CD25/44 expression (column 1) before each subset was analyzed for CD4/CD8 expression (columns 2-5); the post-DN3 cells consist of DN4 (IV), immature single positive (ISP) and DP cells, where the DN4 and ISP cells are rare proliferating blasts that are clearly detectable only by gating on the large cells within the post-DN3 compartment (column 3). Shown is a representative of three mice from a single experiment.
(B) CD4 induction in CD8 cells in the peripheral blood in adult Cd4*/*; rtTA+/+ mice (left) or in Rag2 KO mice adoptively transferred with CD8 cells isolated from Cd4*/*; rtTA+/+ mice (right). Mice were exposed to Dox (1 mg/ml) for 17 days. Blood was drawn from the tail vein at various times and the cells stained for CD4, CD8 and TCR before analysis. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. Each symbol represents a mouse.
(C) TCR activation facilitated rtTA-mediated Cd4 induction in CD8 cells. Peripheral blood cells from Cd4*/*; rtTA+/+ mice were stimulated overnight in vitro with plate-bound anti-CD3/28 (left) or 1 uM ionomycin plus 10ng/ml PMA (right) in the presence of Dox (100ng/ml). CD4 expression in CD8 cells was analyzed.
(D) Cd4*/*; rtTA+/+ mice were exposed to Dox from birth to adulthood before analysis of CD4 expression in the peripheral blood.
(E) Cd4*/*; rtTA+/+ mice were exposed to Dox from conception to adulthood. Dox was then discontinued and CD4 expression in peripheral blood cells monitored, where macrophages/monocyte were identified by their large size.
(F) rtTA induced epigenetic changes at the Cd4 promoter and silencer in peripheral CD8 cells. Cd4*/*; rtTA+/+ mice were exposed to Dox for 1 week (+), and the peripheral CD8 cells expressing CD4 were isolated and analyzed as described in Fig. 3G. CD8 cells from the mice lacking Dox exposure (−) were used as a control. Asterisks indicate statistically significant effects of Dox (p<0.05).