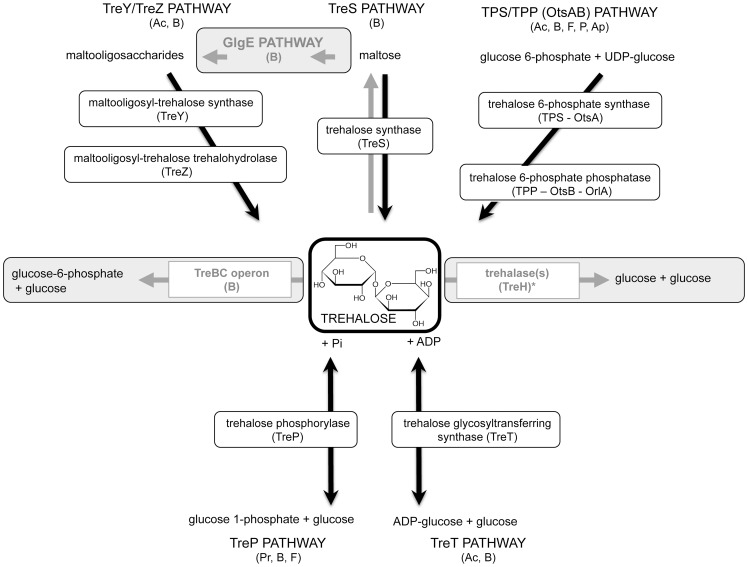
Figure 1. Trehalose metabolic pathways.
Pathways of trehalose synthesis are highlighted in black, and pathways of degradation in grey. Major conserved enzymes are included. The TPS/TPP (OtsAB) is a two-step pathway. Glucose 6-phosphate and UDP-glucose are converted into trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P) by the trehalose 6-phosphate synthase enzymes. T6P is then converted into trehalose by the T6P phosphatase enzymes. The TreYZ pathway yields trehalose from glucans. The first step, operated by TreY (maltooligosyltrehalose synthase), mediates the inversion of the reducing-end glucosyl residue of α-1,4 glucan into α, α-1,1-linked non-reducing trehalosyl disaccharide end. This is followed by the cleavage of free trehalose from the glucan chain by TreZ enzyme (maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase). The TreS pathway consists of the trehalose synthase enzyme (TreS), and converts trehalose into maltose and vice versa. The TreS and the GlgE pathways are linked by the Pep2 enzyme, a maltokinase, that converts maltose into maltose 1-phosphate. The novel GlgE pathway converts trehalose via the TreS pathway into glucans and glycogen in Mycobacterium tuberculosis [33]. From maltose 1-phosphate, the essential maltosyl-transferase GlgE extends glucan chains, and the essential GlgB enzyme introduces α-1,6-linked branches to linear glucans. The TreBC operon consists of TreB, the trehalose PTS permease, which transports extracellular trehalose inside the cells and converts it into T6P. T6P is then converted into glucose 6-phosphate and glucose by TreC enzymes encoding T6P hydrolases. Trehalase enzymes degrade trehalose into two molecules of glucose, and have been categorized as cytoplasmic (or neutral) and extracellular (or acid) enzymes. The role of the TreP and TreT pathways in pathogenicity has not been demonstrated thus far. The TreP pathway is the reversible hydrolysis of trehalose in presence of inorganic phosphate by the trehalose phosphorylase enzyme (TreP). The reversible TreT pathway consists of the formation of trehalose and ADP from ADP-glucose and glucose by the trehalose glycosyltransferring synthase enzyme (TreT). Ac, Archea; B, Bacteria; F, Fungi; P, Plants; Ap, Arthropods; Pr, Protists. * Trehalase is present in all kingdoms, including mammals.