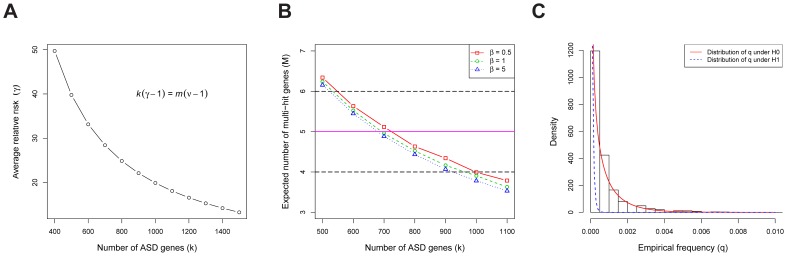
Figure 3. The genetic parameters of ASD.
(A) The relationship between the number of ASD risk genes (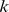 ) and the average relative risk (
) and the average relative risk ( ).
).  stands for the total number of genes in the human genome, and
stands for the total number of genes in the human genome, and  for the fold enrichment of the de novo LoF mutations in probands vs. siblings (about 2 in our data). (B) The expected number of multi-hit genes (
for the fold enrichment of the de novo LoF mutations in probands vs. siblings (about 2 in our data). (B) The expected number of multi-hit genes (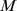 ) in
) in 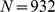 families, as a function of the number of ASD risk genes (
families, as a function of the number of ASD risk genes (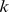 ). The observed
). The observed 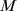 is 5, and we define the plausible range of
is 5, and we define the plausible range of 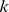 as the values corresponding to
as the values corresponding to 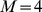 to 6. The model assumes the relative risks of ASD risk genes follow a gamma distribution with the scale parameter
to 6. The model assumes the relative risks of ASD risk genes follow a gamma distribution with the scale parameter 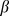 . The variance of the relative risk (
. The variance of the relative risk ( ) across genes equals
) across genes equals 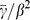 (
( is the average of
is the average of  of all ASD risk genes), which limits the range of plausible values for the model. The estimated value of the average
of all ASD risk genes), which limits the range of plausible values for the model. The estimated value of the average  is approximately 20. (C) For each gene, we compute the empirical allele frequency (
is approximately 20. (C) For each gene, we compute the empirical allele frequency (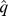 ) of LoFs as the number of LoF variants divided by the sample size. The histogram of the LoF frequencies of all genes is shown. Also shown are the estimated distributions of
) of LoFs as the number of LoF variants divided by the sample size. The histogram of the LoF frequencies of all genes is shown. Also shown are the estimated distributions of 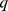 under the null (red, solid line) and the alternative (blue, dashed line) models, respectively.
under the null (red, solid line) and the alternative (blue, dashed line) models, respectively.