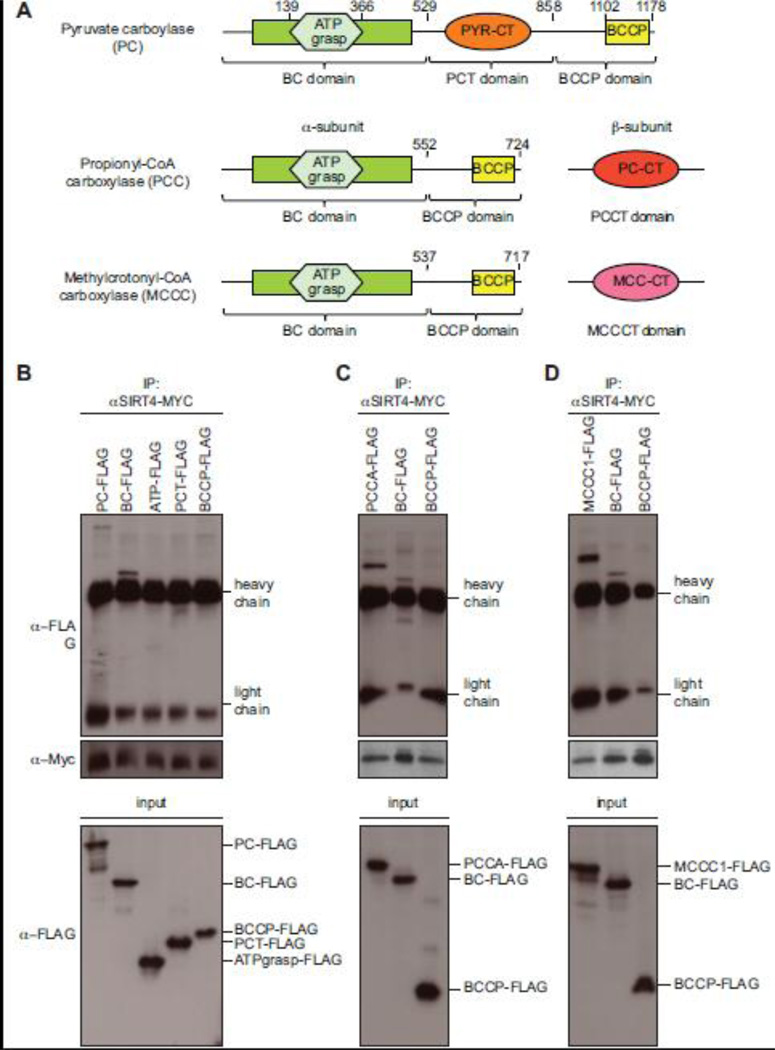
Fig. 5. The biotin carboxylase domain of PC, PCCA and MCCC1 specifically binds to SIRT4.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain organization of mitochondrial biotin carboxylases. All three proteins have a highly conserved N-terminal biotin carboxylase domain (BC) and a C-terminal biotin carboxyl carrier protein domain (BCCP). Brackets indicate the deletion constructs generated to map the region interacting with SIRT4. Domain boundaries of the mutant proteins are indicated by the amino acid positions. Analysis of interaction with PC (B), with PCCA (C) and MCCC1 (D). For co-immunoprecipitation experiments, the indicated FLAG-tagged deletion constructs of the biotin-dependent carboxylases were transiently expressed together with human SIRT4-MYC in HEK293 cells. Equal amounts of immunoprecipitated MYC-tagged SIRT4 were loaded on SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-FLAG and anti-MYC antibodies (top). Cell extracts (input) were directly analyzed in Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibodies to determine expression levels of tagged protein in each experiment (bottom). Running positions of FLAG-tagged proteins and of the antibody’s heavy and light chains are indicated on the right.