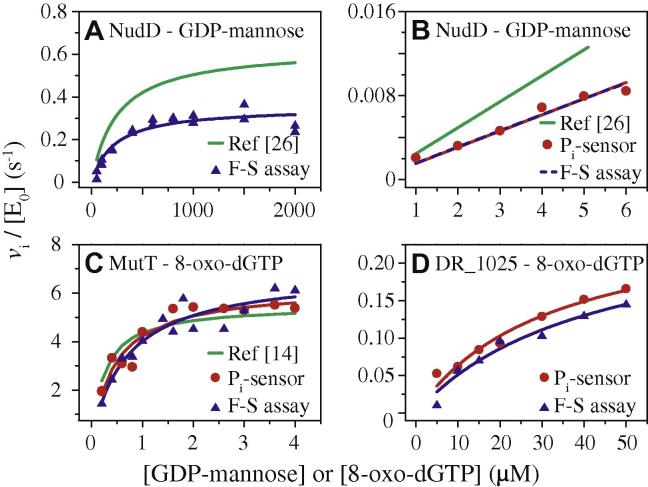
Fig. 2.
Comparison of vi/[E0] (s−1) exhibited by Nudix hydrolases determined by discontinuous assays as measured here and as reported in the literature versus the continuous Pi-sensor assay. Experimental data are shown as dots or triangles, and fitted data are shown as lines. The values of the kinetic parameters are collected in Table 1. (A) Comparison of Fiske–SubbaRow assay (F–S assay, pH 8.5, 37 °C, blue triangles and solid blue line) and calculated data from (A) in Ref. [26] (pH 8.5, 37 °C, solid green line) for NudD-catalyzed hydrolysis of GDP-mannose. (B) Comparison of Pi-sensor assay (pH 8.5, 37 °C, red dots and solid red line), calculated data from Ref. [26] (solid green line), and extrapolated data fitting from the Fiske–SubbaRow assay of panel A to low substrate concentration (blue dashed lines) for NudD-catalyzed hydrolysis of GDP-mannose. (C) Comparison of Pi-sensor assay (pH 7.6, 37 °C, red dots and solid red line), Fiske–SubbaRow assay (pH 7.6, 37 °C, blue triangles and solid blue line), and calculated data from Ref. [14] (pH 8.0, 30 °C, solid green line) for MutT-catalyzed hydrolysis of 8-oxo-dGTP. (D) Comparison of Pi-sensor assay (pH 7.6, 37 °C, red dots and solid red line) and Fiske–SubbaRow assay (pH 7.6, 37 °C, blue triangles and solid blue line) for DR_1025-catalyzed hydrolysis of 8-oxo-dGTP. Coupling enzymes, where used, are listed in Table 1.