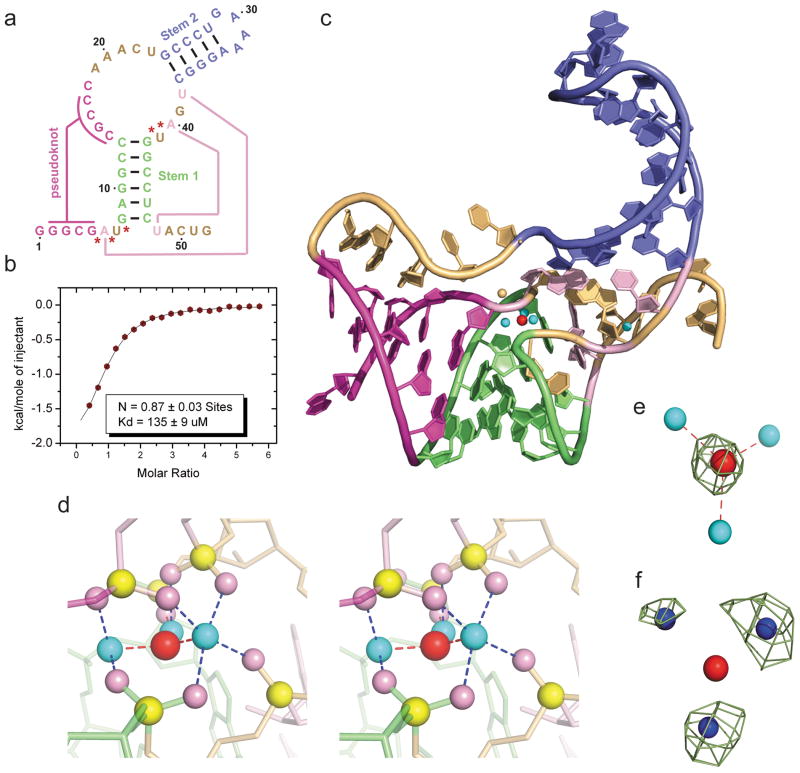
Figure 1. Sequence, binding affinity and structure of the sensing domain of the T. petrophila fluoride riboswitch in the ligand bound state.
a, Secondary structure schematic of the 52-nt sensing domain of the T. petrophila fluoride riboswitch used in this study. The color-coding highlights regular stem segments (blue and green) and long-range pseudoknot pairing interactions (magenta and pink; connected by lines), and bases not involved in pairing interactions (gold). Five phosphates, whose non-bridging oxygens form a shell around the three hydrated metal ions (in cyan), with the metal ions in turn coordinated to the fluoride ion (in red), are labeled by red stars. b, ITC-binding curve for binding of KF to the T. petrophila fluoride riboswitch in 5 mM Mg2+-containing buffer (for experimental conditions, see Methods section). c, 2.3 Å crystal structure of the fluoride riboswitch in the ligand bound state. The color-coding of RNA segments follows that shown in panel a, with the fluoride ion shown by a red ball and directly-coordinated metal ions by cyan balls. d, A close-up stereo view of the ligand-binding pocket in the same perspective as in panel c, with the emphasis on the fluoride ion, three coordinating metal ions and five inwardly-pointing backbone phosphates. e, Fo-Fc omit electron density map contoured a 4σ level calculated following deletion of the fluoride ion. f, Anomalous density at 9σ level at positions of metal ions 1, 2 and 3 for crystals of the complex soaked in 50 mM Mn2+-containing solution.