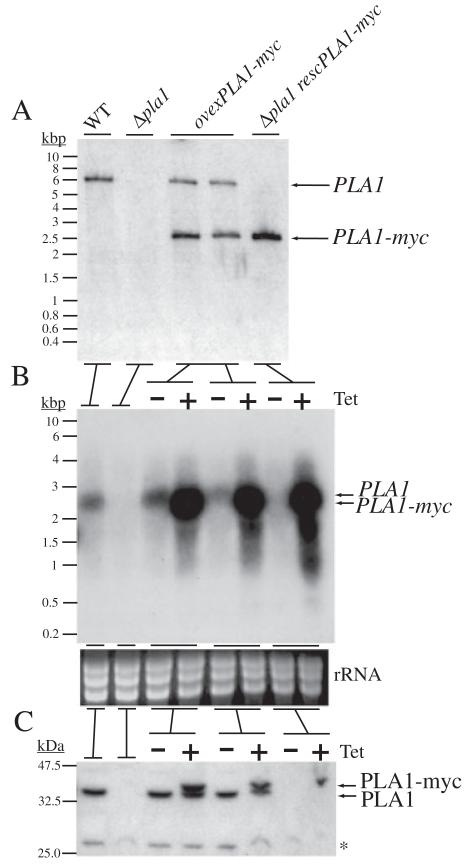
Fig. 4.
Validation and characterization of TbPLA1 mutant cell lines.
A. TbPLA1 null mutants were generated in the procyclic form of T. brucei after sequential TbPLA1 UTR-targeted homologous recombination with UTR-flanked puromycin and blasticidin resistance genes. Cell lines were analysed by Southern blot after digesting genomic DNA with EcoRV. EcoRV-digested T. brucei WT gDNA reveals one size of DNA fragment detectable by fluorescein-labelled TbPLA1 ORF probe. In TbPLA1 null mutant cells (Δpla1) both TbPLA1 alleles are absent. A tetracycline (Tet)-inducible myc-tagged recombinant ectopic copy of TbPLA1 (PLA1-myc) cloned into a phleomycin-resistant pLEW100 cassette was introduced into a different locus in WT gDNA to produce transgenic TbPLA1 overexpression cell lines (ovexPLA1-myc), or introduced in the null mutant gDNA to produce a rescue cell line (Δpla1 rescPLA1-myc).
B. Northern blot analysis of TbPLA1 mutants. Total RNA extracted from WT and TbPLA1 mutant trypanosomes were hybridized with TbPLA1 (top panels), loading controls are also presented (bottom panels).
C. Western blot analysis of cell lysates of TbPLA1 mutants. Both native PLA1 (theoretically 32.4 kDa) and tagged PLA1-myc (theoretically 33.9 kDa) proteins were detected by antibodies raised against the purified recombinant enzyme. * = background bands that show loading in the null mutant lanes.