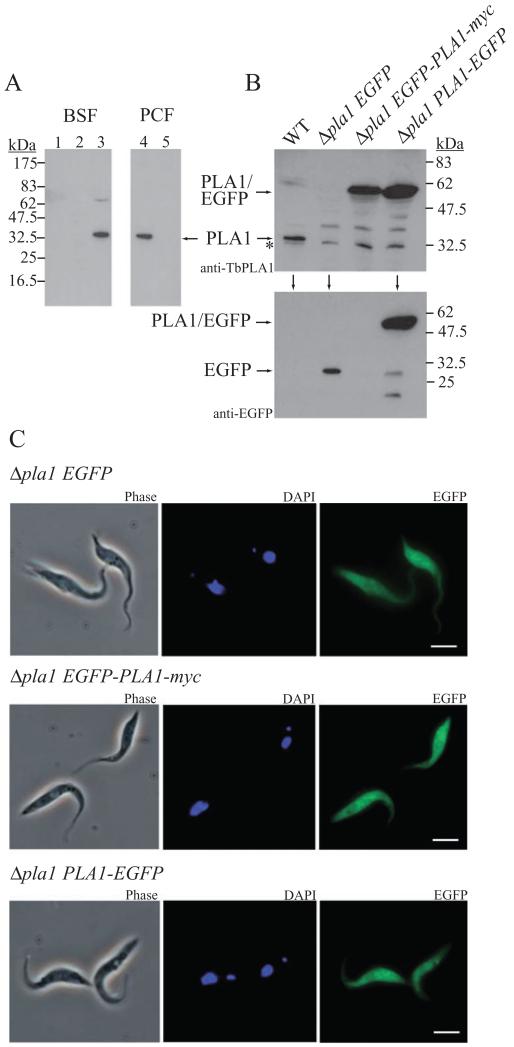
Fig. 7.
Cellular distribution of TbPLA1.
A. Subcellular fractions were prepared as described in Experimental procedures and used in immunoblotting with anti-TbPLA1 antibodies. TbPLA1 is constitutively expressed and was detected in the cytosolic fraction of both BSF and PCF WT cells (lane 3 and lane 4 respectively) but absent from PCF TbPLA1 null mutants (lane 5). TbPLA1 is also absent from the large granular and small granular (microsomal) fractions from BSF WT cells (lane 1 and lane 2 respectively).
B. PCF TbPLA1 null mutant cells transformed with an ectopic copy of an N-terminal EGFP-PLA1 gene fusion (Δpla1 EGFP-PLA1-myc) or a C-terminal PLA1-EGFP gene fusion (Δpla1 PLA1-EGFP) were analysed after tetracycline induction by anti-TbPLA1 (top panel) or anti-EGFP (lower panel) immunoblotting for the presence of expressed fusion protein (~60 kDa). WT cells and null mutants transformed with an ectopic copy of EGFP only (Δpla1 EGFP) serve as negative controls for fusion protein expression. * = background bands just smaller than native TbPLA1 that show loading in the null mutant lane.
C. Analysis of the subcellular localization by immunofluorescence microscopy of both PLA1/EGFP fusion proteins (right panels) compared with EGFP only confirms a cytoplasmic distribution for soluble TbPLA1. PCF transgenic mutants are also shown in phase contrast (left panels) and after DAPI staining (middle panels).