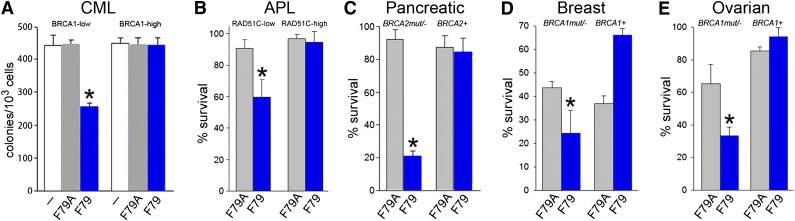
Figure 4.
F79 aptamer induces synthetic lethality in tumor cells displaying genetic BRCA deficiency. (A) Clonogenic activity of GFP+ BRCA1low and BRCA1high UT7-BCR-ABL1 cells transfected with internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-GFP or BRCA1-IRES-GFP constructs untreated (white symbols) and treated with 5 μM F79A (gray symbols) or F79 (blue symbols) aptamer; *P < .001 in comparison with untreated and F79A group. (B) PML-RAR-positive NB4 cells transfected with IRES-GFP (RAD51C-low) and RAD51C-IRES-GFP (RAD51C-high) were treated with 5 μM F79A (gray symbols) and F79 (blue symbols) aptamer. Results represent percentage living GFP+ cells; *P < .001 in comparison with F79A group. (C-E) Cells were irradiated or treated with etoposide and 5 μM F79 (blue) or 5 μM F79A (gray) aptamers, and living cells were counted after 3 to 5 days in Trypan blue. (C) 10Gy γ-irradiated BRCA2-null Capan-1 cells and those with reconstituted BRCA2 expression (BRCA2+), (D) BRCA1-null and BRCA1-reconstituted (BRCA1+) HCC1937 cells, and (E) BRCA1-null and BRCA1-reconstituted (BRCA1+) UWB1.289 cells treated with 5 μM etoposide; *P < .03 in comparison with F79A-treated counterparts.