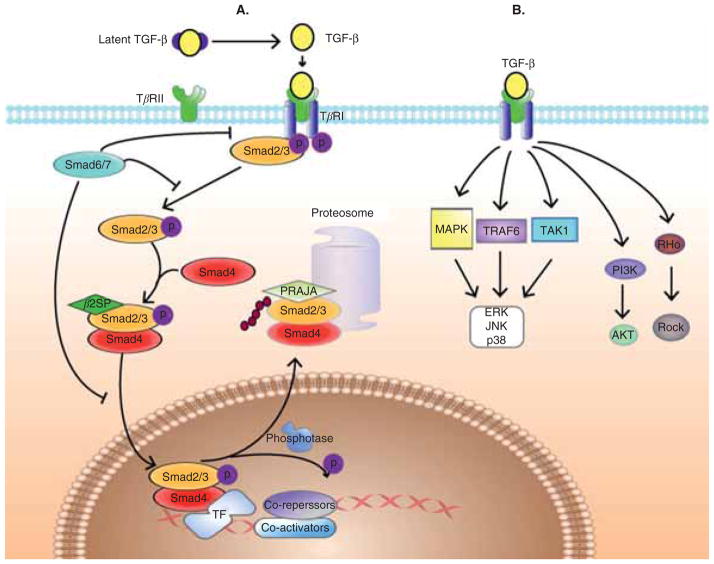
Figure 1. TGF-β signaling pathway.
A. TGF-β ligands signal through distinct receptors and Smads that are modulated by adaptor proteins and ubiquitinators. TGF-β binds to serine threonine kinase receptor complexes that phosphorylate R-Smads as well as adaptor proteins such as β2-spectrin. R-Smads, β2-spectrin and Smad-4 form a heteromeric complex, translocate to the nucleus and regulate target genes expression. At all levels, Smad modulation occurs through adaptor proteins as well as E3 ligases such as PRAJA and Smurfs, generating diverse and complex signals. B. Smad-independent signaling. TGF-β can promote the activity of several signaling pathways other than Smad, including mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs), phosphoinositide 3′ kinase (PI3K), TRAF6-TAK1-p38/JNK, Rho-Rock, among others. Such alternative signal transducers often regulate the Smad pathway.