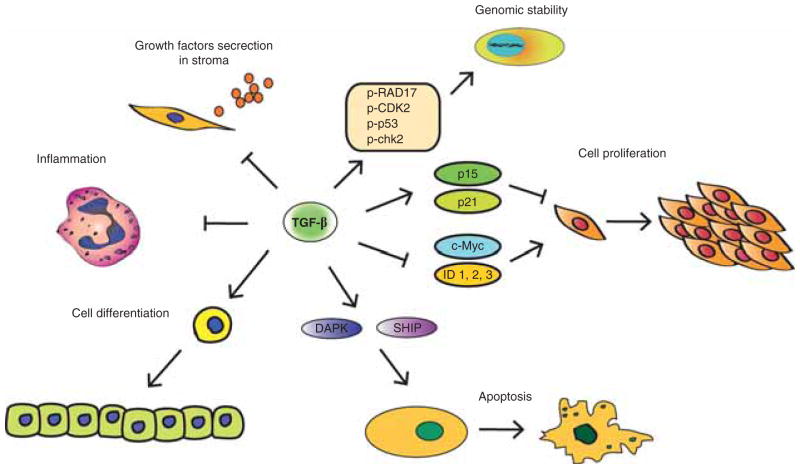
Figure 2. TGF-β signaling in tumor suppression.
TGF-β achieves its tumor suppressive effect by several arms: the most important one is the cytostatic or cell proliferation regulation arm. Here, TGF-β induces expression of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors p21 and p15 and decrease expression of proliferative drivers such as c-Myc and ID. Other modes of TGF-β action include its effects on apoptosis and cell differentiation, genomic stability and indirect effects on the tumor stroma, such as inhibition of growth factors secretion and anti-inflammatory effects.