FIGURE 7.
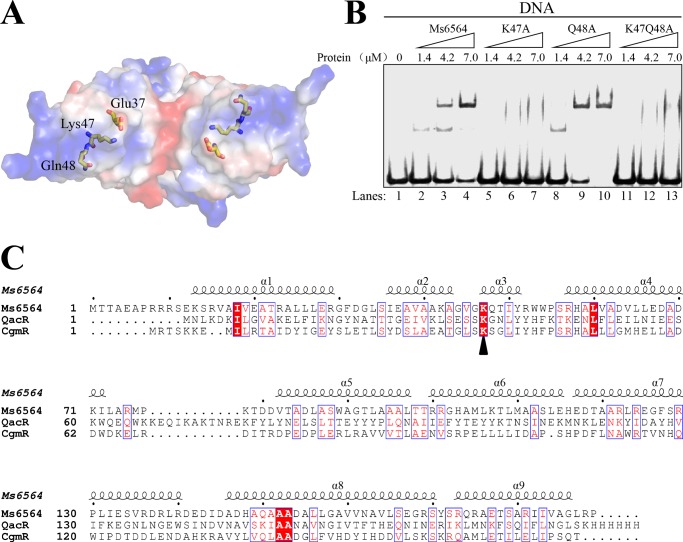
The conserved Lys-47 residue interacts directly with DNA base and is critical for specific DNA binding activity of Ms6564. A, electrostatic surface potential of Ms6564. Electrostatic surface representation of Ms6564 with blue and red regions indicating positive and negative electrostatic regions, respectively. The amino acid residues Glu-37, Lys-47, and Gln-48 are shown as sticks. Note the positively charged Lys-47 and negatively charged Glu-37. B, assays for the DNA binding activity of K47A and Q48A variants of Ms6564. 32P-Labeled DNA substrates were co-incubated with increasing amounts (1.4–7 μm) of wild type or mutant Ms6564 protein and loaded onto 5% polyacrylamide/bis (37.5:1) gels and run at a constant voltage of 100 V. Lane 1, substrate only; lanes 2–4, wild type Ms6564; lanes 5–7, K47A mutant variant of Ms6564; lane 8–10, Q48A mutant variant of Ms6564; lane 11–13, K47Q48A mutant variant of Ms6564. No obviously shifted bands were observed for the K47A variant, whereas clearly shifted bands were observed for the Q48A variant of Ms6564. C, alignment of the amino acid sequence of Ms6564 with those of QacR and CgmR. Conserved residues are boxed and highlighted in red; the conserved lysine located on the N terminus of the recognition helix is marked by a triangle.