FIGURE 6.
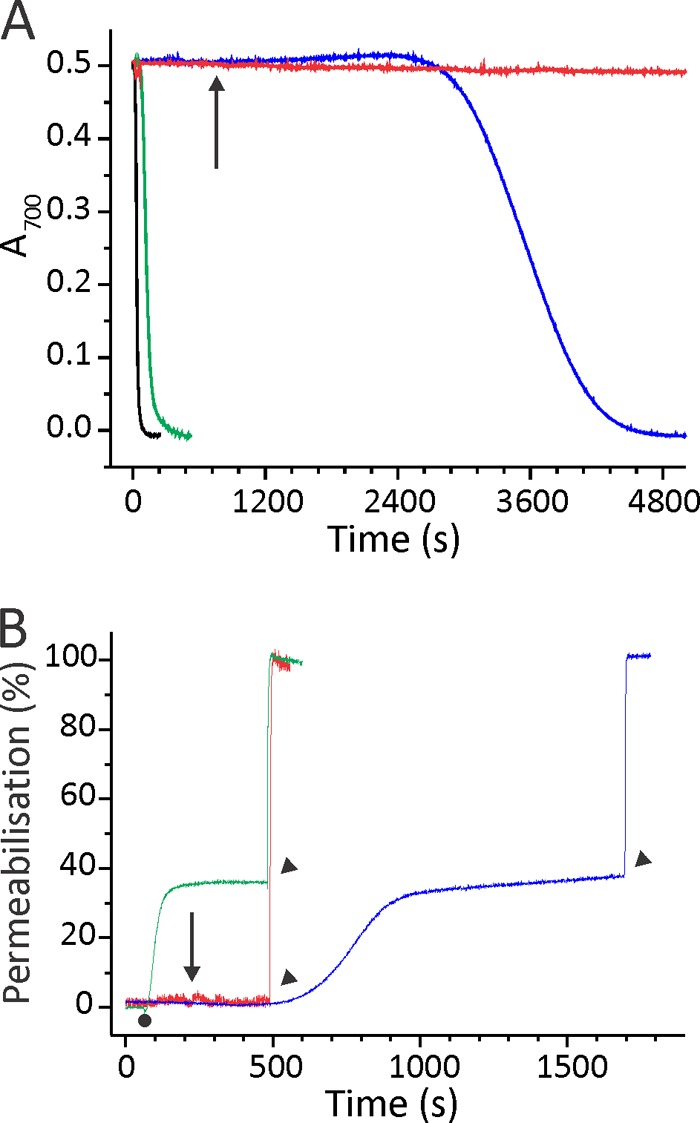
Permeabilizing activity of EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD. A, the restoration of hemolytic activity of EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-OX by the DTT addition. BRBC were stirred in hemolysis buffer at 25 °C. Proteins were added to a final concentration of 7.5 nm. The figure is representative of at least six independent experiments. The reductant DTT was added at a final 2 mm concentration to EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-OX already bound to the membrane (denoted by an arrow). B, permeabilizing activity on calcein-loaded ghosts. Ghosts were stirred in vesicle buffer at 25 °C. The excitation and emission wavelengths were set to 485 and 520 nm, respectively. The addition of 50 nm EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-RED or EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-OX is denoted by a small dot. The percentage of permeabilization was determined at the end of the assay by comparing the fluorescence with the maximal one, obtained by the addition of 2 mm final Triton X-100 (denoted by arrowheads). EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-OX was also reduced after binding to ghosts with final 2 mm DTT (denoted by an arrow) to show that permeabilizing activity is slower in comparison with the protein reduced before binding to ghosts. The figures are representative of four independent experiments. The color code is the same for both panels: green, EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-RED; red, EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-OX; blue, EqtIIV8C,I18C,K69C-NBD-OX reduced with final 2 mm DTT after the protein was bound to the membranes; black, the wild type EqtII.
