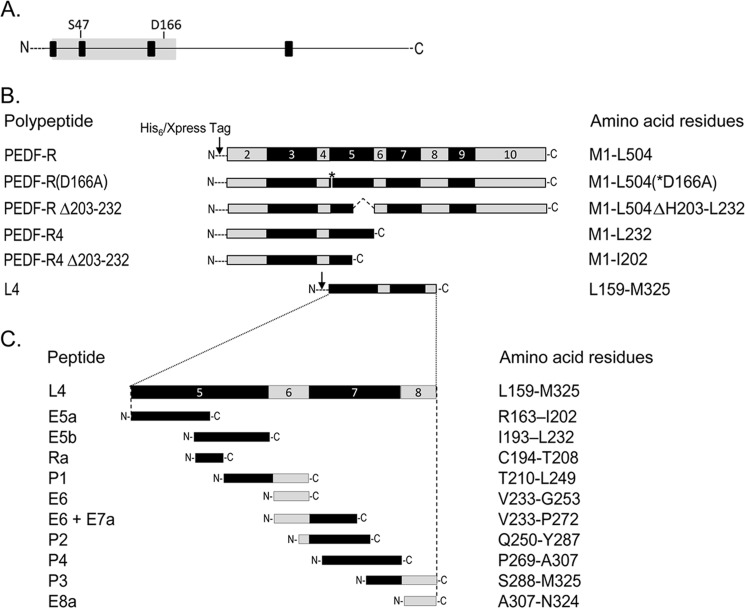
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the PEDF-R constructs and peptides. A, a linear form of the PEDF-R amino acid sequence. Black boxes indicate the locations of the four predicted transmembrane domains, and the gray area indicates the patatin-like phospholipase domain (PNPLA) spanning amino acids 10–179. Locations of the residues that comprise the catalytic site dyad (Ser47 and Asp166) are shown. B, exons (exons 2–10) encoding the PEDF-R polypeptide are illustrated in alternating gray and black code in linear form. The exon numbers are given inside each box. A series of expression constructs for truncated PEDF-R polypeptides is shown. The arrow indicates the position of the His6/Xpress tag fused to the N terminus of PEDF-R fragments. The asterisk denotes the position of the point mutation for D166A. The internally deleted region is indicated by dotted lines. C, design of synthetic peptides spanning L4, the longest extracellular loop of PEDF-R. The names and the amino acid residues comprising each fragment are given to the left and right, respectively, of each fragment. N- and C- indicate the locations of the N and C terminus, respectively.