FIGURE 9.
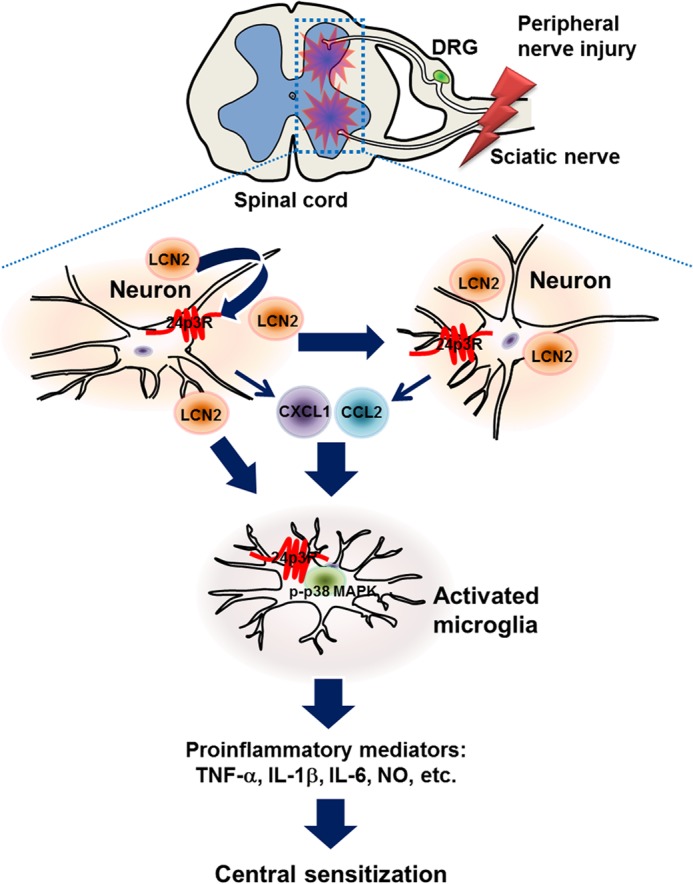
The involvement of LCN2 in the development of pain hypersensitivity following peripheral nerve injury. LCN2 synthesized in spinal neurons after peripheral nerve injury may be released into the extracellular space and bind to 24p3R, which is expressed on the surfaces of neurons and microglia (and astrocytes) in the spinal cord. We surmise that after binding to its receptor, LCN2 could induce the expression and release of chemokines from spinal neurons or other cell types. These chemokines may in turn activate spinal microglia, and thus, facilitate neuroinflammation and the trafficking of other glial and inflammatory cells, ultimately leading to pain sensitization in the spinal cord. Taken together, our findings suggest that the LCN2-chemokine axis plays a central role in the development of pain hypersensitivity under conditions such as neuropathic pain.
