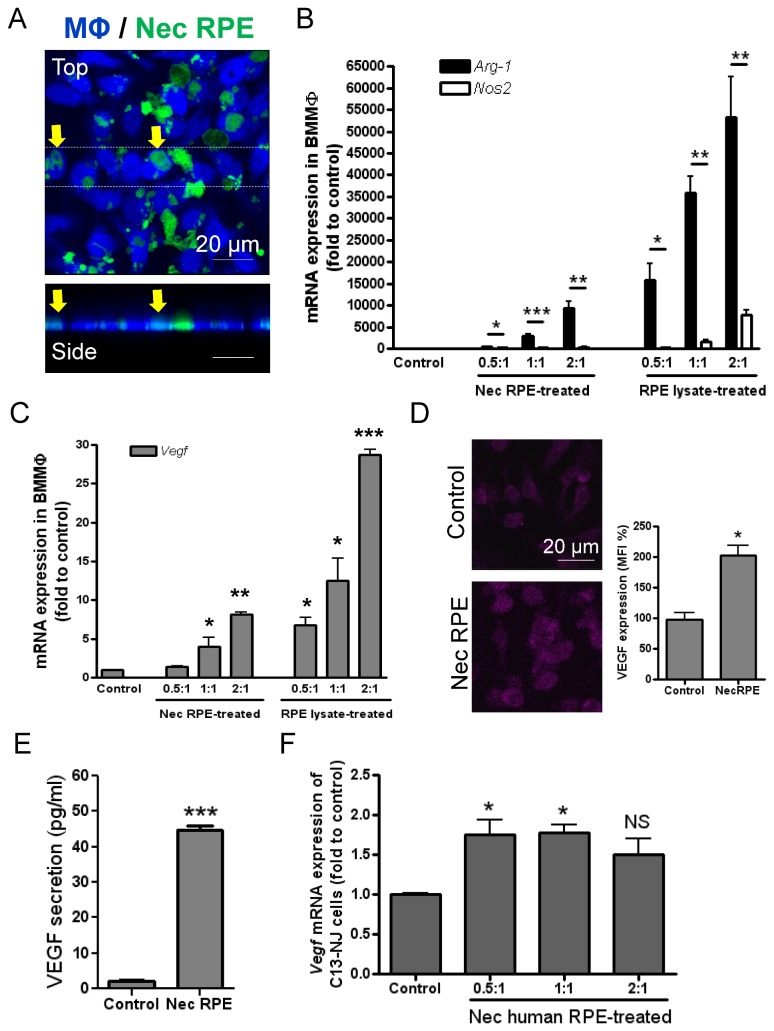
Figure 6. Macrophage uptake of necrotic RPE or its derivatives altering their inflammatory and proangiogenic phenotype.
(A) Necrotic RPE was produced from CFDA-labelled B6-RPE07 cells (green) by heating at 95°C for 15 minutes, while RPE lysate was generated by sonication for 5 minutes on ice. Necrotic RPE cells or lysate were then added to Violet Tracer-labelled BMMΦs at different ratios (RPE to BMMΦ). After 1 hour incubation, the cells were washed, fixed and observed by confocal microscopy. Top and side view of confocal images shows engulfment of dead RPEs/debris by BMMΦs. BMMΦs were collected after 24 hours of incubation with necrotic RPE or cell lysate and RNA was extracted for QRT-PCR analysis to determine Arg-1 and Nos2 (B), and Vegf gene expression (C). 18s rRNA was used as a normalising control. (D) Confocal images and MFI analysis of VEGF immunocytochemistry on BMMΦs treated with necrotic RPE. (E) In some of experiments, after 1 hour of incubation of BMMΦs with necrotic RPE, un-engulfed dead RPE cells and its derivatives were removed and BMMΦs were further cultured for 24 hours and cell culture supernatants collected for determination of VEGF concentration using ELISA. (F) Human microglia cells (C13-NJ cell line) were treated with heat-induced necrotic ARPE19 cells at different ratios for 24 hours and then examined for Vegf mRNA expression. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n≥3. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001 Arg-1 vs. Nos2 (B), or vs. control. NS, not significant.