Figure 2. Docking approach using ray casting.
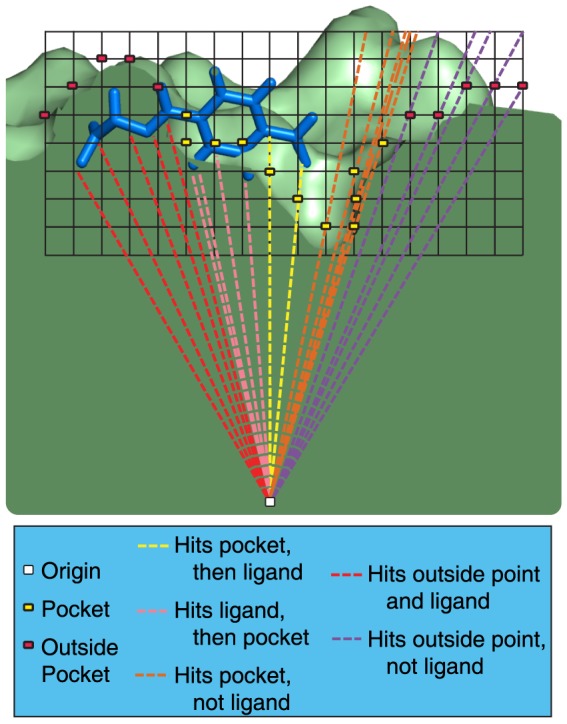
A schematic diagram of DARC scoring is shown in cross section. A grid is placed at a region of interest on a protein surface, and used to identify “deep pocket” points. Points that are not in direct contact with the protein surface are removed, leaving behind a set of points that map the topography of the protein surface pocket (yellow squares). An adjacent layer of points on the protein surface are then labeled “forbidden” points (red squares). Rays are cast from an origin point within the protein (white square) at each pocket point and forbidden point. To score a docked pose, the same rays are cast at the ligand (blue), and the first intersection (if any) is calculated. The contribution to the total score from each ray is dependent on whether the ray was defined based on a pocket point or a forbidden point, and whether the ray intersects this point before or after it intersects with the ligand. These conditions are described in detail in the main text.
