Figure 6.
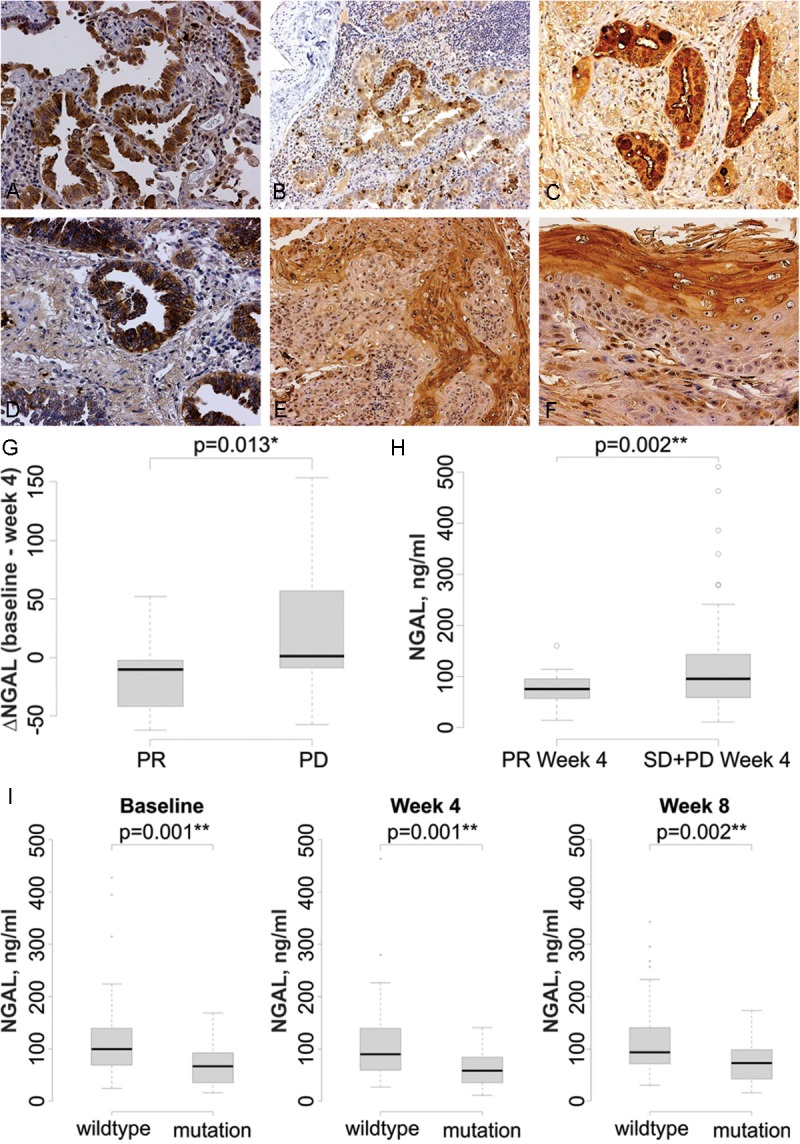
NGAL is detected in lung cancer specimens and is elevated in patients who do not respond to erlotinib. NGAL expression is detected by immunohistochemistry in the in situ component of adenocarcinoma (A) and the invasive component of adenocarcinoma (B). C: NGAL is present in the cytoplasm of mucin-producing cells, as well as in the surrounding regions, in a mucinous invasive adenocarcinoma. D: Strong cytoplasmic NGAL staining in non-mucinous invasive adenocarcinoma. E: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma. F: Greater expression in the keratinizing portion of an invasive squamous cell carcinoma. The magnification is 200X in A, C, D and F and 100X in B and E. G. Change in serum NGAL levels after erlotinib treatment. Following 4 weeks of treatment NGAL levels were significantly decreased in the PR group and increased in the PD group. H: In patients that had a PR, the 4 week plasma NGAL level is significantly lower than that in SD+PD patients (p = 0.002). I: Plasma NGAL levels are lower in patients with mutant EGFR at baseline (**p = 0.001), week 4 (**p = 0.001) and week 8 (***p = 0.002) compared to patients with wild type EGFR.
