Figure 1. The vitamin K cycle.
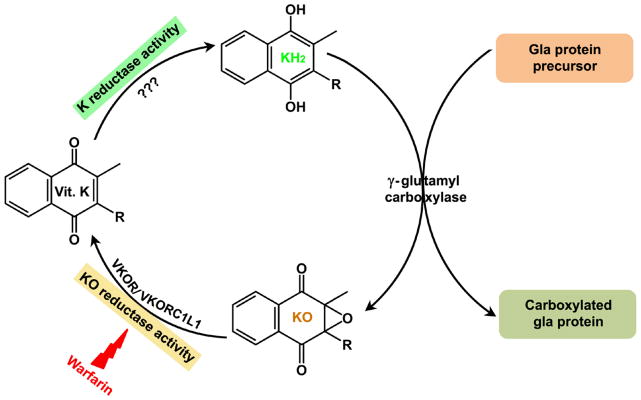
During vitamin K-dependent carboxylation, the reduced form of vitamin K (KH2) is oxidized to vitamin K epoxide (KO) by γ-glutamyl carboxylase. KO is reduced to vitamin K by VKOR or VKORC1L1 (based on this study) (KO reductase activity). This reaction is sensitive to warfarin inhibition. The reduction of vitamin K to KH2 (K reductase activity) is carried out by as yet unidentified enzyme.
