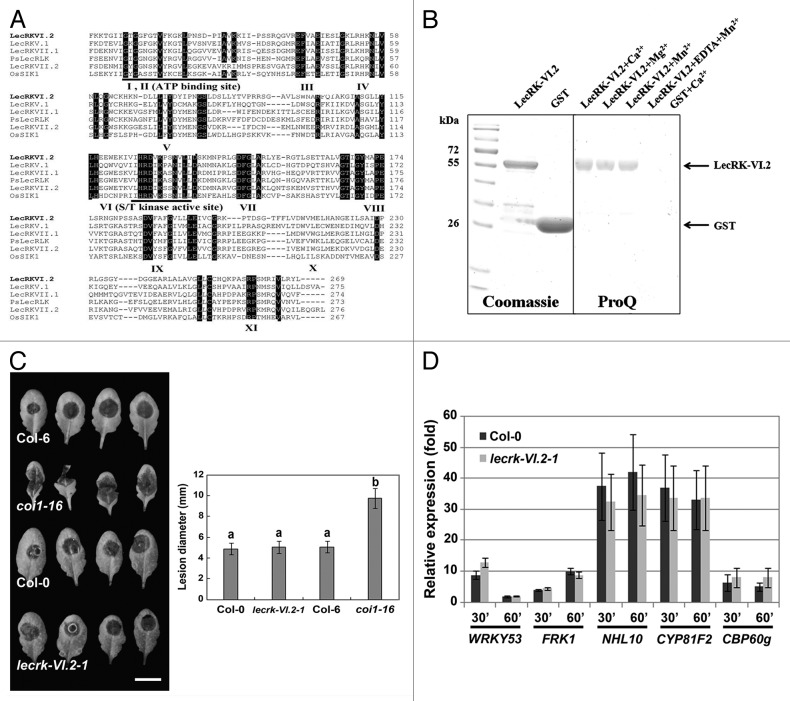
Figure 1.LecRKVI.2 is a functional protein kinase and is dispensable for Arabidopsis resistance to B. cinerea. (A) Alignment comparison of the predicted amino acid sequences of LecRK-VI.2 with 3 Arabidopsis LecRKs (LecRK-V.1, LecRK-VII.1 and LecRK-VII.2), the rice OsSIK1 and the pea PsLecRLK. Sequences above the Roman numerals in black boxes indicate the 11 sub-domains characteristic of a typical protein kinase. (B) Expression and purification of LecRK-VI.2-KD from E.coli using affinity resin and phosphorylation assay. The GST-fusion protein was stained with Coomassie blue and confirmed by peptide sequencing. GST was used as a control (left panel). GST fusion protein LecRKVI.2-KD (2 µg) was incubated with ATP for 30 min in the presence of 5 mM MnCl2, 5 mM CaCl2 or 5 mM MgCl2. Phosphorylation signal was observed with ProQ Diamond phosphoprotein gel staining (right panel). (C) B. cinerea disease symptoms. Arabidopsis leaves were droplet-inoculated and symptoms were visualized 2 d later. Experiments were repeated 3 times with similar results. Bar = 1 cm. Error bars are SD (n = 18 leaves). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences compared with the wild-type Col-0 (LSD test; p < 0.05). (D) Relative expression levels of WRKY53, FRK1, NHL10, CYP81F2 and CBP60 g were analyzed 30 and 60 min after chitin infiltration (50 µg/ml). EF-1 and UBQ10 were used for normalization. Relative gene expression levels were compared with buffer control (defined value of 1) by qRT-PCR analyses. The values are the means ± SD of three biological replicates (n = 9). No significant differences to wild-type Col-0 were observed when based on a t-test (p < 0.01).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.