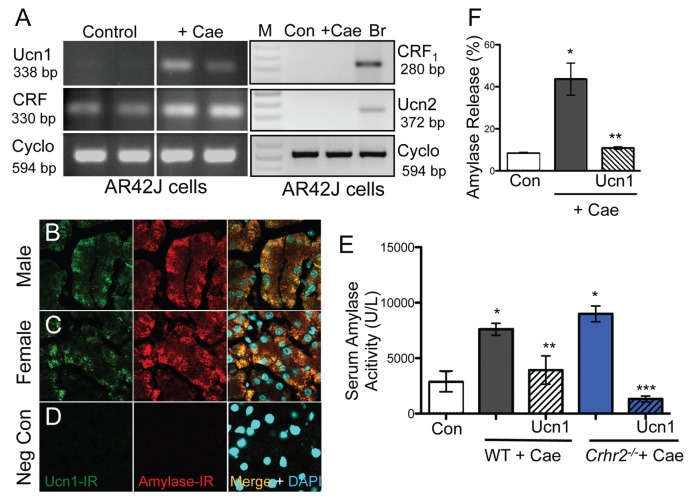
Figure 3.
Ucn1 colocalizes with amylase in acinar cells. Ucn1 mRNA was induced de novo in acinar AR42J cells treated with 10−7 mol/L caerulein for 1 h. CRF mRNA expression was present under basal conditions and was not induced de novo. Ucn2 and CRF1 mRNA were not detected at baseline (Con) or after caerulein treatment in acinar cells, but were present in brain (Br) mRNA. Cyclophilin was used as a normalization control (A). Caerulein treatment increased amylase-IR in acinar cells in WT mice and colocalized with Ucn1-IR in male and female mice (B, C), respectively (63×); sections stained without any primary antibody served as negative controls (D). Serum amylase activity increased over basal (control) levels (*p < 0.05) in WT (grey bars) and Crhr2−/− (blue bars) mice (E), and Ucn1 treatment (hashed grey and blue bars) significantly decreased amylase release (**p < 0.05 versus WT; ***p < 0.05 versus Crhr2−/−). Amylase release from AR42J cells (F). Caerulein treatment increased amylase release (*p < 0.05) and 10−7 mol/L Ucn1 treatment decreased release (**p < 0.05). Statistical analyses were by ANOVA. Data represent mean ± SEM of three replicates per group.