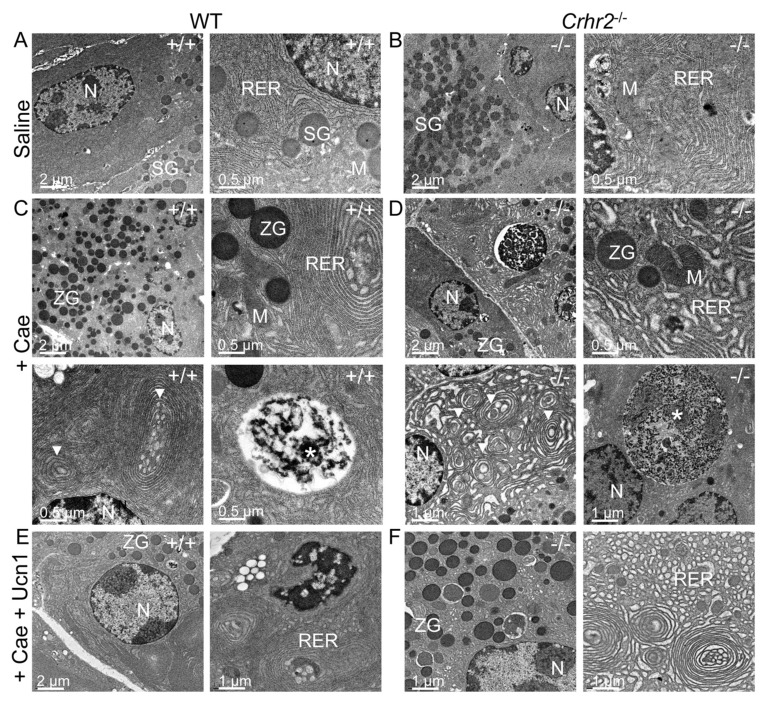
Figure 4.
CRF2 is central to the maintenance of organelle integrity and the endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. Representative electron microscopy (EM) shows normal acinar cell ultrastructure in saline-treated WT (A) or saline-treated Crhr2−/− (B) mice (n = 4/group) with normal appearing acinar cell ultrastructure. During pancreatitis, WT male mice show a marked increase in zymogen granule (ZG) formation, mild expansion of rough ER and intraluminal material (C), consistent with ER stress. Infrequent, small autophagic bodies (*) containing densely staining material were found. During pancreatitis, Crhr2−/− mice show markedly dilated rough ER (D); ER whorls and increased intraluminal inclusion bodies were visible, all of which were increased relative to what was seen in WT pancreatitis. Frequent, multiple large autophagic bodies (white *) that contained numerous ribosomes and membrane components were seen. (M, mitochondria; N, nucleus; RER, rough endoplasmic reticulum; SG, secretory granules; ZG, zymogen granule). Exogenous Ucn1 treatment during pancreatitis markedly reduces ER ultrastructure damage and number of autophagic bodies in both WT and Crhr2−/− male mice (E, F).