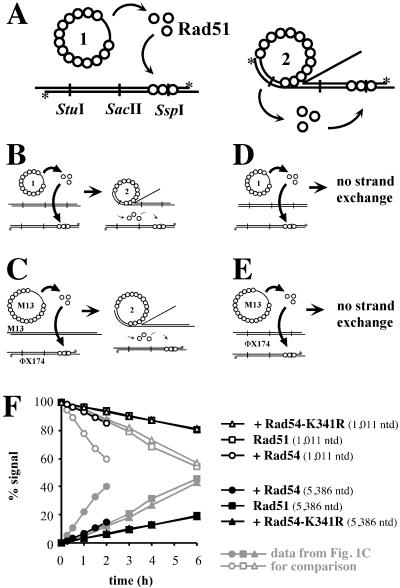
Figure 2.
Control experiments for hDNA extension assay. Control reactions to measure the amount of inhibition of the restriction endonucleases due to the relocalization of Rad51 protein to the dsDNA. (A) Relocalization of Rad51 protein from ssDNA to dsDNA might occur either spontaneously (Right) or may be enhanced during DNA strand exchange (Left). (B–E) To determine the amount of signal in the hDNA extension assay, which corresponds to uncleaved dsDNA analyzed on a denaturing gel because of interference by Rad51 protein relocating on dsDNA, four types of control reactions were performed: in the presence of ongoing DNA strand exchange (B + C) and in the absence of DNA strand exchange (D + E). (B + D) Reactions contained blunt-ended dsDNA (linearized with FspI and labeled at the 5′ ends by polynucleotide kinase as indicated with asterisks), which could not participate in DNA strand exchange (ref. 58 and data not shown). The unlabeled dsDNA was either digested with PstI (B) to enable DNA strand exchange or with FspI (D) to preclude DNA strand exchange. (C + E) Control experiments with heterologous M13mp19 ssDNA. (C) Reactions with ongoing DNA strand exchange contained circular M13mp19 ssDNA and PstI linearized M13mp19 dsDNA. (E) Reactions without DNA strand exchange contained circular M13mp19 ssDNA and PstI linearized ΦX174 dsDNA. The relocalization of Rad51 protein was monitored with a radioactively end-labeled (*) ΦX174 dsDNA linearized with PstI. (F) Graphical representation of data from control reactions as in E by using SspI restriction endonuclease. To reactions with Rad51 protein and Rpa, storage buffer (Rad51 control) (□, ■), Rad54 (○, ●), or Rad54-K341R (▵, ▴) protein was added. All results were obtained in the same manner as in Fig. 1, and the data from Fig. 1C are indicated in gray for comparison.