Figure 5. RA Controls Limb Tbx5 Independently of Heart Isl1.
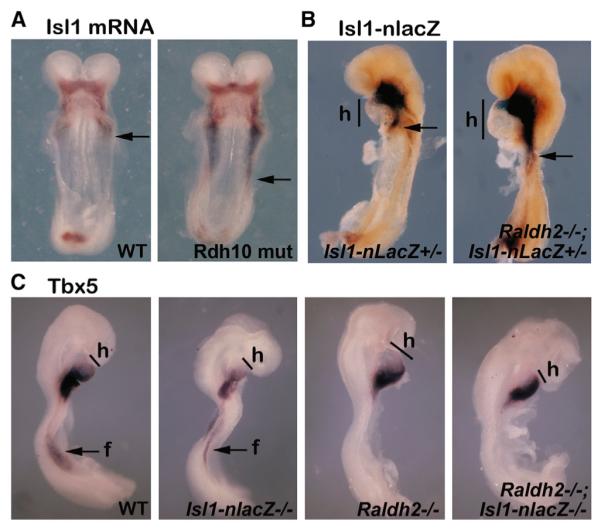
(A–C) E8.5 mouse embryos analyzed by in situ hybridization (A and C) or stained with X-gal to detect Isl1-nlacZ expression (B).
(A) Isl1 mRNA in Rdh10 mutant (Rdh10 mut) versus wild-type (WT) embryos (ventral view). Arrows represent the posterior boundary of the heart field.
(B) Isl1-nlacZ expression in Raldh2−/−;Isl1-nlacZ+/− versus Isl1-nlacZ+/− embryos. Arrows represent the posterior boundary of the heart field (h).
(C) Assessment of heart expansion (h) and forelimb field Tbx5 expression (f) in wild-type, Isl1-nlacZ−/−, Raldh2−/−, and Raldh2−/−;Isl1-nlacZ−/− embryos.
See also Figures S4 and S5.
