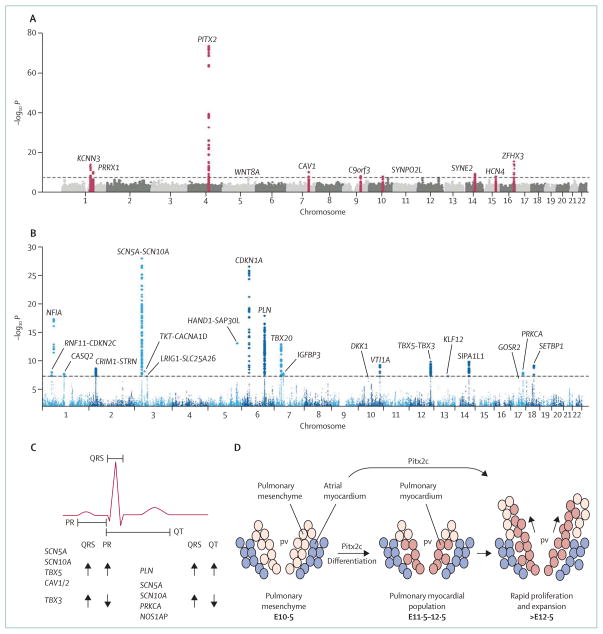
Figure 3. Genome-wide association studies for arrhythmias and cardiac conduction.
(A) Results of a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of patients with lone atrial fibrillation.59 In this Manhattan plot, the x-axis represents the genomic coordinates of each single-nucleotide polymorphism and the y-axis is the negative logarithm of the association p value (the higher the number, the greater the significance). The dashed line shows the threshold for genome-wide significance (p<5 × 10−8). So far, three major genes (KCNN3, PITX3, and ZFHX3) and seven additional loci close to genes for ion channels, or associated with cardiopulmonary development or signal transduction, have been identified.59 (B) Manhattan plot of association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms with QRS duration in genome-wide association meta-analysis of 40 407 individuals from 14 studies.60 22 loci reached genome-wide significance. (C) Effects of genome-wide study-identified variants on the electrocardiogram.60 Many variants that prolong the PR interval are also associated with increased QRS duration, whereas variants associated with prolonged QRS are associated with a shortened QT interval. (D) Pitx3, an atrial fibrillation candidate gene, is necessary for the development of the pulmonary myocardium. Pulmonary mesenchyme differentiates into myocardium and expands to form a sheet around the pulmonary vein branches (E10·5–12·5, mouse gestation in days).61 (A) is reproduced from reference 59, by permission of Patrick Ellinor and Nature Publishing Group; (B) and (C) are reproduced from reference 60, by permission of Nona Sotoodehnia and Nature Publishing Group; (D) is reproduced from reference 61, by permission of Wolters Kluwer Health. pv=pulmonary vein. Pitx2c=Pitx2 isoform c.