Figure 3.
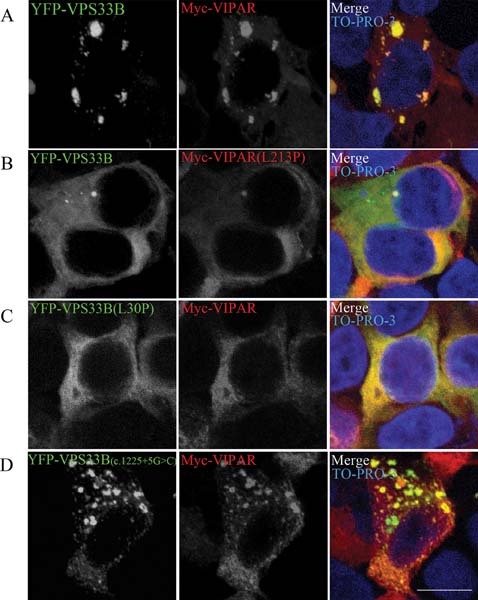
VPS33B and VIPAR interaction. Confocal fluorescence photomicrographs of HEK293 cells cotransfected with wild-type and mutant constructs of YFP-tagged VPS33B and Myc-tagged VIPAR. Wild-type YFP-VPS33B and Myc-VIPAR colocalized (A). However, constructs modeled on severe phenotype mutant proteins (B) Myc-VIPAR(L213P) and (C) YFP-VPS33B(L30P) resulted in a disruption of VPS33B–VIPAR interaction. D: Transfection for YFP-VPS33B(c.1225G>C), modeling an attenuated phenotype, resulted in partial colocalization. Myc-VIPAR was immunostained with mouse monoclonal antibody anti-myc (Sigma) at a 1:400 concentration and anti-mouse ALEXA-568 conjugate secondary antibody (Invitrogen) at a concentration of 1:400. Nuclei are stained with TO-PRO-3. Scale bars, 10 μm.
