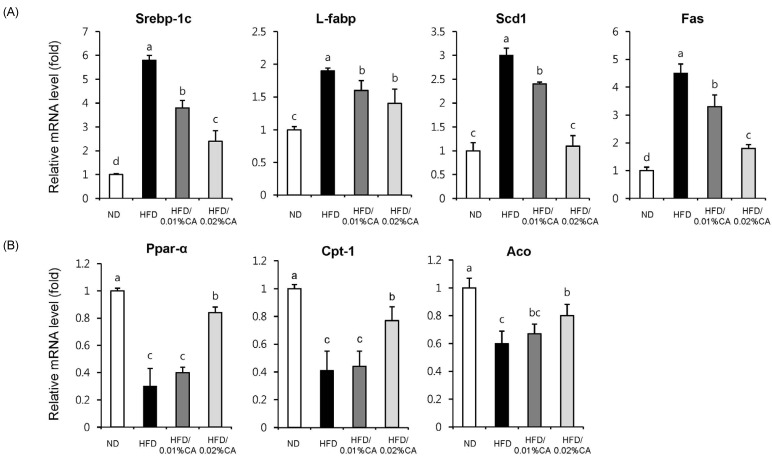
Fig. 5.
Effects of carnosic acid supplementation on hepatic mRNA expression of genes related to fatty acid synthesis and β-oxidation in high-fat diet-fed mice. Mice were fed a normal diet (ND) or a high-fat diet (HFD), alone or supplemented with 0.01% (w/w) carnosic acid (CA) or 0.02% (w/w) CA (HFD + CA) for 12 weeks. Consequently, the following four groups of mice (n = 10, each) were examined: control ND group (white), HFD group (black), HFD supplemented with 0.01% (w/w) CA group (dark grey), and HFD supplemented with 0.02% (w/w) CA group (light grey). Analysis of hepatic expression of various genes was performed using real-time PCR, and expression levels were normalized to β-actin. Expression levels of (A) lipogenic genes (Srebp-1c, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; L-fabp, liver-fatty acid binding protein; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; Fas, fatty acid synthase), and (B) β-oxidation-related genes (Ppar-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α; Cpt1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; Aco, acyl CoA oxidase) are represented here. Values are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 10). Bars with different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05) from one another.