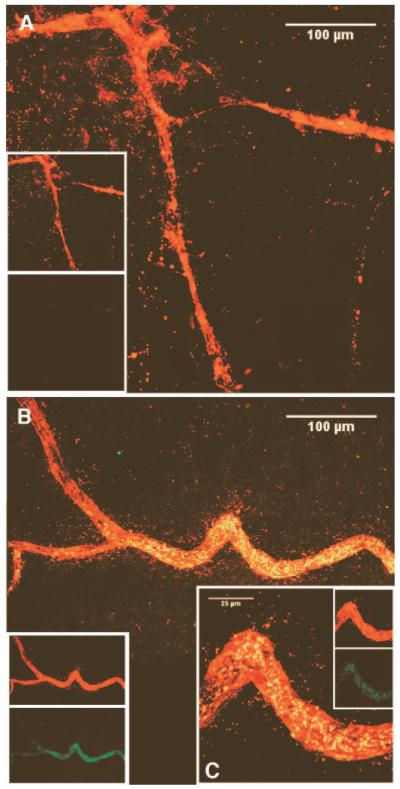
FIG. 1.
Injection of huCD34+ cells within the vitreous results inreendothelialization of damaged vessels in the mouse model of OIR. Green-labeled huCD34+ cells were administered to mouse pups (n = 8) on P12 and eyes harvested at P14. Images are z-series projections of two-color LSCM. Panel A depicts the central region of a retina from a mouse that did not receive huEPC, and shows expected pathology, including lack of microvessels and degenerate larger vessels. Panel B depicts a similar region of a retina from a mouse eye that was injected with huEPC. Note the high degree of incorporation of labeled cells into the dilated and functioning vessel (yellow). Inset panel C is a higher magnification of a portion of the vessel in panel B. The other insets show separate red and green channels used to make the composite images.